Understanding Food Intolerances
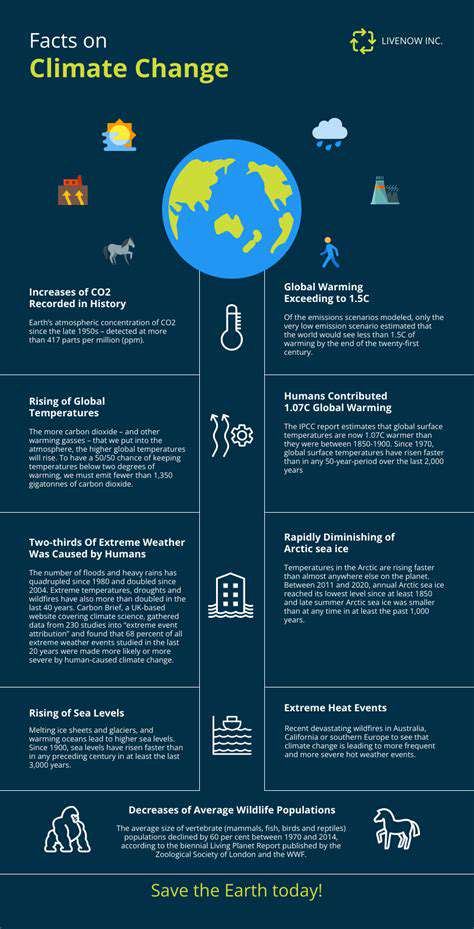
Food intolerances are a common health concern, impacting millions worldwide. They differ from allergies, typically involving an immune system response, and instead often manifest as digestive discomfort. Recognizing the signs and symptoms is crucial for effective management and preventing further complications. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of these reactions is key to developing personalized strategies for symptom alleviation. Intolerances can range from mild digestive upset to more severe conditions, making early identification and intervention vital.
Various factors can contribute to food intolerance development, including genetic predisposition, environmental influences, and even the presence of certain gut bacteria. It's important to remember that not all digestive issues stem from intolerance; other factors like poor dietary choices, stress, or infections can also play a role. Thus, a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Common Symptoms and Triggers
Symptoms of food intolerance can vary significantly, but common complaints include bloating, gas, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, and nausea. These symptoms can range in severity and may not appear immediately after consumption, making identification challenging. Furthermore, the specific foods responsible for the reactions can differ from person to person.
Common triggers for food intolerances include lactose, gluten, fructose, and certain food additives. Lactose intolerance, for example, results from a deficiency in the enzyme lactase, hindering the digestion of lactose, a sugar found in dairy products. Gluten intolerance, often associated with celiac disease, can trigger an immune response in sensitive individuals. Identifying these triggers through careful dietary tracking and consultation with a healthcare provider is crucial for managing symptoms.
Other potential triggers may include histamine-rich foods, sulfites, and preservatives, further highlighting the complexity of food intolerances and the need for personalized approaches to diagnosis and management.
Diagnosis and Management Strategies
Diagnosing food intolerances often involves a combination of methods, including detailed dietary histories, symptom questionnaires, and potentially, elimination diets. A healthcare professional can guide individuals through these processes, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation to differentiate between various digestive issues and accurately identify potential triggers.
Management strategies for food intolerances primarily focus on identifying and avoiding trigger foods. This often involves careful reading of food labels, seeking out alternative ingredients, and educating oneself about hidden sources of problematic substances. Dietary modifications and lifestyle adjustments play a significant role in alleviating symptoms and improving overall health. In some cases, supplements or medications may also be recommended to manage specific symptoms or support digestive health.
Ultimately, managing food intolerances requires a personalized approach tailored to individual needs and symptoms. Working closely with a healthcare professional is crucial for developing a sustainable and effective plan for symptom relief and overall well-being.
Algorithms are fundamental to computer science, providing a structured set of instructions for solving specific problems. They are essentially recipes that dictate how data should be processed and manipulated to achieve a desired outcome. Understanding these core concepts is crucial for anyone seeking to work with or design software solutions.
Diagnosing Food Sensitivities: A Multifaceted Approach
Identifying Potential Triggers
A crucial first step in diagnosing food sensitivities is pinpointing potential triggers. This often involves a detailed food diary, meticulously recording everything consumed, including the timing, quantity, and preparation method of each food item. Careful observation of symptoms following meals is equally important. This meticulous documentation can reveal patterns and potential correlations between specific foods and adverse reactions, helping to narrow down the list of possible culprits.
Beyond the obvious, consider less obvious triggers like processed foods, additives, and even cross-contamination in shared preparation areas. Understanding your dietary habits and environment is key to identifying potential sources of irritation. This proactive approach significantly aids in focusing diagnostic efforts.
Exploring Symptoms and Reactions
Recognizing the range of symptoms associated with food sensitivities is vital. These can manifest in various ways, from digestive issues like bloating, gas, and diarrhea to skin problems such as hives, eczema, or rashes. Headaches, fatigue, and even mood swings can also be indicators. The variety of symptoms can sometimes make identification challenging, highlighting the need for a comprehensive approach to diagnosis.
Paying attention to the timing of symptoms relative to food consumption is critical. Sometimes, reactions might be delayed by several hours or even days. This delayed response can complicate the identification process, making it essential to maintain a thorough record of both food intake and associated symptoms.
The Role of Elimination Diets
Elimination diets, a cornerstone of diagnosing food sensitivities, involve temporarily removing suspected trigger foods from the diet. This allows the body to rest and potentially recover from the negative effects of the food. Over time, the elimination diet can help to pinpoint specific foods that trigger reactions.
Close monitoring of symptoms during the elimination phase is crucial. This is where the meticulous food diary becomes invaluable. Careful tracking and documentation of reactions will help in accurately identifying which foods are causing issues. This method, while potentially restrictive, can be a highly effective tool for identifying sensitivities.
Considering Diagnostic Tests
While elimination diets are a powerful starting point, some individuals may benefit from further diagnostic testing, such as blood tests or stool analysis. These tests can help to identify specific immune responses to certain foods, providing additional insights into potential sensitivities. However, it's important to remember that these tests can sometimes be inconclusive or yield false positives.
Consulting with a registered dietitian or allergist is recommended to interpret the results of such tests and to determine the best course of action based on individual needs and circumstances. Proper interpretation and guidance are crucial for making informed decisions about dietary management.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Ultimately, seeking guidance from a healthcare professional, such as a registered dietitian or allergist, is essential in the diagnosis of food sensitivities. Their expertise in understanding the complexities of the human body and potential food interactions is invaluable.
These professionals can help develop a personalized plan, including dietary recommendations and strategies to manage symptoms. They can also provide valuable insights into the potential role of other factors that might contribute to digestive issues or other symptoms. A professional consultation is often the most effective way to receive a comprehensive and tailored approach to diagnosing and managing food sensitivities.