Industrialized Animal Agriculture and its Ethical Implications
Modern industrialized agriculture's factory farming model prioritizes output and financial gains above all else, often at the expense of animal wellbeing. These operations, marked by extreme confinement systems, routinely inflict substantial distress on livestock. The staggering number of creatures subjected to these conditions demands we scrutinize the moral consequences, while exploring ways to alleviate suffering through improved husbandry practices. Typical features include severely restricted movement spaces, denial of species-specific behaviors, and elevated disease risks from overcrowding. A comprehensive assessment of this approach proves vital for grasping its full consequences, both for animal welfare and potentially public health.
Beyond the visible animal distress, factory farming raises broader ethical questions. Its intensive methods frequently degrade ecosystems through chemical runoff, excessive resource use, and habitat destruction. The routine administration of antibiotics to prevent disease in cramped conditions contributes to antimicrobial resistance - a growing human health crisis. Such systems also consume disproportionate amounts of water and feed crops, compounding their environmental footprint. Addressing these interconnected ethical and ecological impacts becomes imperative for creating responsible food production networks.
Alternatives to Factory Farming and the Path Forward
Given factory farming's dominance, exploring alternative livestock production methods becomes essential. Shifting toward humane, sustainable agriculture requires coordinated efforts across multiple fronts: advancing ethical farming techniques, informing consumers, and implementing supportive policies. Potential solutions span from traditional pasture-based operations to cutting-edge technologies designed with animal welfare as a priority.
Transforming current systems demands active participation from all stakeholders. Shoppers wield tremendous influence through purchasing decisions, while education initiatives help people understand different production methods' consequences. Legislators must foster sustainable agriculture through appropriate regulations and research funding. Ultimately, moving beyond industrial animal farming necessitates society-wide collaboration - a collective undertaking crucial for establishing food systems that respect both animals and ecosystems.
Regenerative agricultural models, emphasizing environmental harmony and animal dignity, offer promising alternatives. Investigating traditional practices like rotational grazing alongside innovative approaches could yield more compassionate and ecologically sound food production methods. This transition requires rethinking societal values - acknowledging animals' inherent worth and our responsibility toward ethical nourishment.
The Role of Consumer Choices in Shaping Animal Welfare
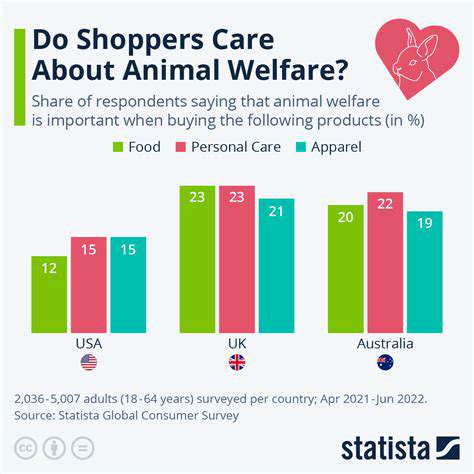
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Buying habits continue evolving, influenced by cultural changes, technological progress, and economic factors. Businesses must comprehend these dynamics to adjust their approaches and maintain relevance. Organizations that accurately predict and address these shifts frequently secure substantial competitive benefits. This applies across industries - from changing culinary tastes to rising demand for ethically sourced goods.
Market patterns frequently mirror broader social transformations. For instance, heightened health consciousness reshapes purchasing decisions regarding food, beverages, exercise gear, and personal items. Enterprises must therefore analyze these developments carefully to align products with contemporary expectations.
The Impact of Price and Value
Cost remains fundamental to purchase decisions. Shoppers consistently seek optimal returns on expenditure, comparing alternatives extensively. True value extends beyond price tags, incorporating perceived quality, functionality, and overall satisfaction.
Consumers meticulously evaluate worth before buying, balancing benefits against expenses. Companies that clearly articulate their offerings' advantages tend to attract and keep customers more successfully.
The Power of Brand Loyalty and Trust
Brand allegiance significantly affects consumer behavior. Those developing confidence in specific labels tend to remain faithful customers. Such loyalty generates recurring sales and enthusiastic recommendations - invaluable assets for business expansion. Establishing and preserving positive brand perception remains vital for nurturing consumer confidence.
Trust correlates directly with product reliability and excellence. Customers prefer continuing relationships with brands they consider honest and consistent. This confidence often encompasses corporate ethics and social responsibility commitments.
The Influence of Marketing and Advertising
Strategic promotional campaigns profoundly impact consumer preferences. Well-targeted messaging that resonates with particular demographics can effectively alter perceptions and boost transactions. Thoughtful marketing implementation can transform how products are viewed and stimulate demand.
The Role of Availability and Accessibility
Product availability critically influences purchasing choices. Consumers favor conveniently obtainable items, whether through digital platforms, retail outlets, or alternative distribution methods. Accessibility significantly affects decisions, with readily available options typically receiving preference. Companies must optimize their supply chains to serve target markets effectively.
The Importance of Consumer Feedback and Reviews
Customer evaluations substantially guide purchase considerations. Favorable assessments encourage potential buyers, while negative commentary may deter them. Review aggregations function as collective opinions, shaping attitudes and influencing market directions. Enterprises actively responding to feedback gain crucial insights for product refinement.
Exploring Marrakech's vibrant souks or Tokyo's luminous avenues, one inevitably encounters the irresistible sights and smells of street cuisine. This transcends mere convenience eating - it represents profound cultural immersion bridging global communities. Street food's magic lies in transforming humble components into memorable encounters through centuries of culinary tradition. Each vendor guards unique recipes like family treasures, embodying their culture's essence.
The Interconnectedness of Ethical Concerns in Food Production
The Foundation of Ethical Frameworks
Moral structures, whether individual or organizational, originate from core principles that inform choices. These fundamentals typically emerge from cultural traditions and communal beliefs, forming our moral compass. Comprehending these bedrock values proves essential for constructing coherent ethical systems. This foundation operates as a navigational tool, steering us toward morally aligned actions.
Philosophical traditions including utilitarianism, Kantian ethics, and Aristotelian virtue theory provide distinct methodologies for interpreting and implementing moral standards. Each viewpoint offers specialized analytical tools for assessing conduct and results, underscoring ethics' inherent complexity. Examining these varied approaches enhances ethical literacy and promotes nuanced reasoning.
The Impact of Technology on Ethical Considerations
Technological progress introduces unprecedented ethical dilemmas. Challenges surrounding AI, digital privacy, and automated systems require careful deliberation regarding their societal ramifications. Confronting these emergent issues necessitates anticipatory, cooperative strategies that develop ethical protocols alongside technological breakthroughs.
The digital domain frequently obscures conventional privacy and responsibility boundaries. Preserving ethical norms in this fluid environment requires adaptable regulations and moral frameworks capable of evolving with technological change. Safeguarding disadvantaged groups and ensuring equitable tech access constitute fundamental aspects of conscientious innovation.
Interconnectedness with Societal Values
Ethical issues remain deeply enmeshed with cultural beliefs and social mores. Religious perspectives, historical contexts, and community standards all contribute to defining appropriate conduct. Acknowledging diverse value systems proves critical for building mutual understanding and facilitating cross-cultural ethical discussions.
Moral conflicts often emerge when competing values intersect. Resolving such predicaments demands cultural sensitivity and commitment to finding mutually acceptable solutions. This interconnectedness underscores the need to contemplate wider social implications when making ethical determinations.
The Role of Individuals in Maintaining Ethical Standards
Ultimately, ethical preservation depends equally on institutions and private citizens. Personal morals and conscience shape daily choices and behaviors. By developing strong personal ethics, we collectively foster a more principled society.
Active involvement in moral discourse and social issues proves vital for positive transformation. Individuals contribute meaningfully to ethical progress by championing justice and integrity.