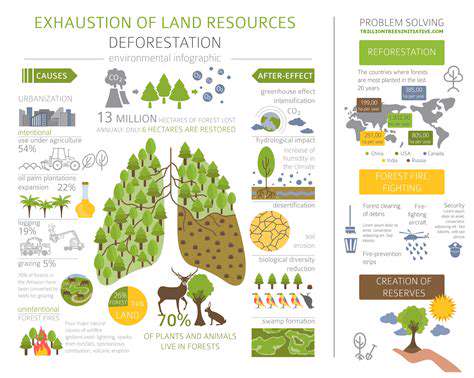
Minimizing Deforestation Impacts
Deforestation, the clearing of forests for other land uses, has profound consequences for both ecosystems and human communities. The loss of biodiversity is staggering, with countless species losing their habitats and entire ecosystems thrown into disarray. Trees play a critical role in carbon absorption, and their removal accelerates climate change. Additionally, deforestation leads to soil degradation, making land unsuitable for agriculture and threatening local livelihoods.
Implementing sustainable land management is no longer optional—it's imperative. Reforestation projects, eco-friendly farming techniques, and strict enforcement against illegal logging must become global priorities. When we balance human development with environmental stewardship, we create a future where both can thrive together.
Sustainable Agriculture Practices
The agricultural sector must evolve to reduce its environmental footprint while maintaining productivity. Methods like conservation tillage preserve soil structure and prevent erosion. Agroforestry systems, which combine crops with trees, offer multiple benefits: they provide shade, improve soil quality, and reduce pressure to clear new farmland.
These innovative approaches don't just protect forests—they create more robust farming systems. Healthier soil retains water better, requires fewer chemical inputs, and ultimately produces higher yields. This sustainable model proves that environmental responsibility and agricultural success can go hand in hand.
Reforestation and Afforestation Initiatives
Tree-planting projects serve dual purposes: restoring damaged landscapes and creating new forests. Reforestation focuses on areas that were previously wooded, while afforestation introduces trees to new locations. Both strategies help capture carbon, support wildlife, and regulate water cycles.
The key to success lies in thoughtful implementation. Choosing native species suited to local conditions ensures better survival rates. Involving community members in planting and maintenance fosters long-term commitment. When done right, these green initiatives can transform barren areas into thriving ecosystems.
Role of Policy and Legislation
Governments must establish clear frameworks to combat deforestation. Effective policies should prohibit destructive logging while incentivizing sustainable alternatives. Without proper enforcement, even the best regulations remain meaningless.
Creative solutions like tax benefits for sustainable landowners or grants for reforestation can drive change. When policy aligns with environmental goals, it creates powerful momentum toward forest conservation. This top-down approach, combined with grassroots efforts, can significantly slow deforestation rates.
Community Engagement and Awareness
Local populations often hold traditional knowledge about sustainable land use. Empowering these communities through education and resources transforms them into forest guardians. When people understand how deforestation affects their daily lives, they become motivated to protect their environment.
Public education campaigns can shift societal attitudes toward conservation. Highlighting the connection between healthy forests and clean air, stable climate, and reliable water supplies makes the issue personal. This groundswell of awareness creates the cultural change needed for lasting environmental protection.
Conserving Water Resources: A Crucial Aspect of Sustainability
Understanding the Importance of Water Conservation
Water sustains all life on Earth, yet many fail to appreciate its scarcity. Our growing population and changing climate strain water supplies like never before. Conserving water isn't just about saving money—it's about ensuring survival for future generations. The complex interplay between water systems, weather patterns, and ecosystems demands our careful attention.
Water underpins all ecological processes, from supporting diverse species to regulating global temperatures. Neglecting conservation disrupts these delicate balances, with consequences that ripple through both natural and human systems. Protecting water resources means protecting the foundation of life itself.
The Impact of Climate Change on Water Availability
Climate disruption creates unpredictable water patterns—intensifying droughts in some areas while causing floods in others. These extremes challenge traditional water management approaches. Understanding how climate change affects the water cycle is essential for developing adaptive strategies.
As precipitation becomes less reliable and temperatures rise, innovative solutions become critical. Modernizing infrastructure, developing water-efficient technologies, and creating flexible distribution systems will help communities weather these changes. The challenge is immense, but so are the opportunities for innovation.
Effective Water Conservation Strategies for Households
Simple household changes yield significant water savings. Low-flow fixtures, prompt leak repairs, and rainwater collection systems make conservation effortless. When millions adopt these practices, the cumulative effect transforms water usage patterns.
Industrial and Agricultural Water Management Practices
Agriculture and industry account for most water use worldwide. Implementing precision irrigation, water recycling systems, and drought-resistant crops can dramatically reduce consumption. These sectors must lead the way in water innovation.
Advanced technologies like soil moisture sensors and closed-loop industrial systems set new efficiency standards. Investing in water-smart technologies today ensures sustainable production tomorrow. This proactive approach benefits businesses and the environment alike.
The Role of Policy and Public Awareness in Water Conservation
Effective conservation requires coordinated efforts. Government policies should reward water efficiency while discouraging waste. Public education campaigns help citizens understand their role in preserving this precious resource.
When communities value water conservation, they demand and support smart policies. This virtuous cycle of awareness and action creates lasting change. Together, policy and education form the backbone of sustainable water management.

Improving Soil Health and Preventing Erosion: A Long-Term Benefit
Improving Soil Structure for Enhanced Water Retention
Healthy soil forms the foundation of sustainable agriculture. By increasing pore space, soil better absorbs and retains moisture—reducing runoff while nourishing plants. This natural water management decreases irrigation needs and makes farms more drought-resistant.
Techniques like cover cropping and composting transform poor soil into fertile ground. These methods mimic natural processes, building soil structure gradually but sustainably. The result is land that produces abundantly while withstanding environmental stresses.
Preventing Erosion Through Effective Management Practices
Soil erosion threatens food security and water quality worldwide. Contour farming, terracing, and windbreaks offer proven solutions. These techniques work with the landscape rather than against it, slowing water and wind that would otherwise carry soil away.
Contour plowing follows natural elevations, creating mini-dams that trap water. Terraces turn steep slopes into productive farmland. Windbreaks shield fields from destructive gusts. Together, these methods preserve precious topsoil for future generations.
Long-Term Benefits of Sustainable Soil Management
Investing in soil health pays dividends across multiple fronts. Healthier soil produces higher yields with fewer inputs, boosting farmer incomes. Reduced erosion means cleaner rivers and lakes, benefiting entire ecosystems.
Perhaps most importantly, healthy soil acts as a carbon vault—helping mitigate climate change. This unsung hero of environmental protection demonstrates how sustainable agriculture can address multiple challenges simultaneously. By nurturing our soils today, we ensure they can continue supporting life for centuries to come.
The transition to sustainable soil management represents one of our most promising opportunities. It offers solutions to food insecurity, water pollution, and climate change—all while improving farmers' bottom lines. This comprehensive approach to land stewardship creates lasting value for both people and the planet.