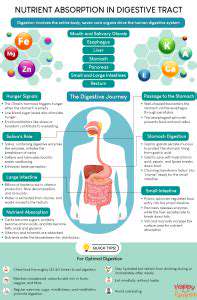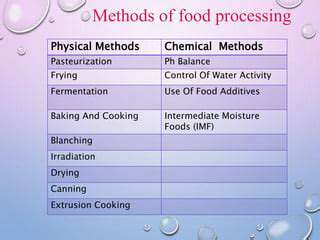
Nutrient Degradation Mechanisms
Nutrient loss during food processing is a multifaceted issue, encompassing a range of mechanisms that can lead to significant reductions in the nutritional value of food products. These mechanisms are often complex and interconnected, making it challenging to isolate the specific factors responsible for any particular nutrient loss. Heat treatments, for example, can cause the denaturation of proteins and the degradation of vitamins, while mechanical processes can lead to the physical separation and loss of valuable components.
Impact on Vitamin Content
Vitamins are particularly susceptible to degradation during processing. High temperatures, exposure to oxygen, and the presence of certain chemicals can all contribute to vitamin loss. For instance, heat-induced oxidation can lead to the breakdown of vitamin C, while exposure to light can cause the degradation of vitamin A. These losses can be substantial, and their impact on overall health can be significant.
Mineral Losses in Processed Foods
Minerals are also vulnerable to loss during food processing. Washing and blanching procedures, in particular, can lead to significant leaching of minerals like calcium, iron, and potassium into the water. Furthermore, the use of certain processing aids can chelate or bind minerals, rendering them unavailable for absorption in the body. This loss of essential minerals can have a negative impact on various bodily functions.
Effect of Processing Methods
Different processing methods have varying impacts on nutrient retention. Traditional methods, such as fermentation, often result in the preservation of nutrients. However, modern methods like high-pressure processing and irradiation, while potentially effective in extending shelf life, can also result in some nutrient loss. Understanding the specific impact of each processing method is crucial for developing strategies to minimize nutrient loss.
Factors Affecting Nutrient Retention
Several factors influence the extent of nutrient loss during processing. Processing time, temperature, and the specific ingredients used in the process all play a role. Optimizing these parameters can significantly reduce nutrient loss and improve the nutritional quality of the final product. Careful consideration of these factors is essential for maintaining the nutritional value of processed foods.
Minimizing Nutrient Loss Strategies
Strategies to minimize nutrient loss during processing are becoming increasingly important. These include using milder processing techniques, controlling processing temperatures, and employing appropriate packaging and storage methods. Implementing these strategies is crucial for maintaining the nutritional value of processed foods and ensuring the safety and quality of our food supply. Innovation in these areas is ongoing, leading to the development of improved techniques and technologies for enhanced nutrient retention.
Preservation Techniques and Nutritional Impact

Preservation Methods for Food Safety
Food preservation techniques are crucial for maintaining the safety and quality of food products, preventing spoilage and extending shelf life. Proper preservation methods not only ensure that food remains edible but also play a vital role in reducing food waste, a significant global concern. Understanding the fundamental principles behind these methods is essential for effective food preservation and safe consumption.
Preservation methods often involve controlling factors that promote microbial growth, such as temperature, moisture, and oxygen levels. By manipulating these factors, we can create an environment less favorable for microorganisms to thrive, thereby extending the shelf life of food products.
Understanding the Principles of Food Preservation
The core principles behind various preservation methods revolve around inhibiting or eliminating the growth of microorganisms, enzymes, and other factors responsible for food spoilage. This involves creating a hostile environment for these harmful agents through methods that alter the food's physical or chemical properties.
Understanding the specific needs of different types of food is key to selecting the most appropriate preservation technique. Different foods have varying levels of susceptibility to spoilage, depending on their composition and inherent properties.
Thermal Processing Techniques
Thermal processing techniques, such as pasteurization and sterilization, are frequently used for preserving a wide range of food products. These techniques involve heating food to specific temperatures for a set duration to destroy or significantly reduce the number of harmful microorganisms and enzymes.
High temperatures effectively inactivate microorganisms, preventing spoilage and extending the shelf life of the food. However, the precise temperature and time parameters must be carefully controlled to ensure food safety and maintain desirable sensory qualities.
Chemical Preservation Methods
Chemical preservation methods utilize specific chemicals to inhibit microbial growth and extend the shelf life of food products. These chemicals often function by altering the pH level or creating an environment unsuitable for the growth of microorganisms. However, the use of chemical preservatives must be carefully regulated to ensure food safety and avoid potential health concerns.
Some commonly used chemical preservatives are meticulously monitored by regulatory bodies to ensure they are safe for human consumption and do not pose undue health risks. Thorough research and testing are critical to validate their effectiveness and safety profile.
Refrigeration and Freezing
Refrigeration and freezing are widely used methods for preserving food by slowing down or halting the growth of microorganisms and enzymatic activity. By lowering the temperature, the metabolic processes of spoilage organisms are significantly reduced, thereby inhibiting their growth and extending the shelf life of the food.
Freezing, in particular, can preserve food for much longer periods than refrigeration. The freezing process creates a solid-state environment in which microbial activity is greatly reduced, allowing for prolonged storage. Proper freezing techniques are critical to maintain the quality and safety of the preserved food.
Drying and Dehydration
Drying and dehydration methods remove moisture from food products, creating an environment inhospitable for microbial growth. Reduced water activity inhibits the growth of microorganisms and enzymes, thereby preventing spoilage and extending the shelf life of food. The removal of moisture also concentrates the food's nutrients and enhances its stability.
This method is particularly effective for preserving fruits, vegetables, and other perishable foods. This technique is crucial in areas with limited access to refrigeration or freezing, ensuring food availability and reducing food waste.