The Role of Hydration in Health
Proper hydration is crucial for numerous bodily functions, from regulating temperature to transporting nutrients. Maintaining adequate fluid intake is essential for overall health and well-being, impacting everything from cognitive function to physical performance. Dehydration can lead to fatigue, headaches, and impaired concentration, highlighting the vital role that liquids play in our daily lives.
The human body is largely composed of water, and this water plays a vital part in virtually every biological process. Sufficient hydration ensures that cells function optimally, supporting processes like nutrient absorption and waste removal. Without enough liquid, these processes can be disrupted, potentially leading to a range of health complications.
Liquid Intake and Dietary Needs
Different liquids contribute to our overall hydration and dietary needs in various ways. Water is the fundamental liquid, providing essential hydration without extra calories or added sugars. However, other beverages like milk, juice, and even certain soups provide vital nutrients and electrolytes, contributing to a balanced diet.
Understanding the nutritional content of different liquids is important. For example, milk provides calcium and protein, while fruit juices can offer vitamins and antioxidants. However, it's crucial to be mindful of added sugars and calories in some beverages to maintain a healthy diet. Choosing the right liquids is important to ensure a balanced and healthful intake of nutrients.
The Impact of Liquids on Physical Performance
Liquids are fundamental to maintaining optimal physical performance. Adequate hydration is essential for athletes and individuals engaged in strenuous activities, as it allows for efficient nutrient delivery and waste removal. Proper hydration can significantly improve endurance and reduce the risk of heat-related illnesses. Dehydration can lead to fatigue, muscle cramps, and reduced performance, underlining the importance of liquid intake during physical activity.
Staying hydrated is vital during exercise. The body loses fluids through sweat, and replenishing those fluids is key to maintaining optimal performance. Choosing the right hydration strategy, including the right types of liquids, is critical for sustained performance.
Liquid Consumption and Disease Prevention
Certain liquids can contribute to disease prevention. For example, adequate water intake is associated with a reduced risk of kidney stones, and certain herbal teas may offer antioxidant benefits. Drinking enough fluids can help maintain a healthy urinary system and support overall wellness. However, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your liquid intake, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
The impact of liquids on overall health extends to disease prevention. Some liquids contain elements that may help reduce the risk of certain conditions. Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential for personalized advice on liquid intake, particularly for people with specific health needs.
Mastering the Science of Gluten Development (or its Absence)
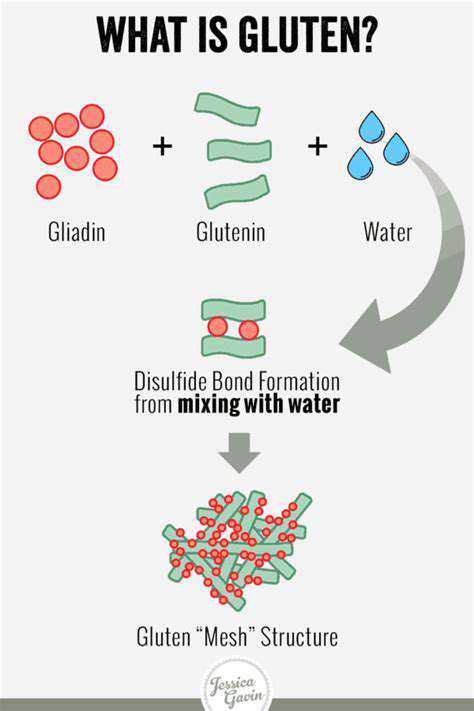
Understanding Gluten's Impact on the Body
Gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, has a significant impact on the digestive systems of many individuals. It's crucial to understand that gluten's effect varies greatly from person to person, and some people can tolerate it without any issues, while others experience severe reactions. For those with celiac disease or non-celiac gluten sensitivity, gluten can trigger inflammation and damage the small intestine, leading to a range of digestive and other health problems. Understanding these variations in response is key to making informed dietary choices.
This complex interaction between gluten and the body's immune system is a key area of research, and ongoing studies provide valuable insights into the mechanisms at play. While the exact mechanisms are not yet fully understood, the potential long-term health implications are substantial, and understanding them is crucial for developing effective dietary strategies and preventative measures.
Gluten-Free Diets: A Comprehensive Overview
Adopting a gluten-free diet is a significant lifestyle change, requiring careful planning and execution. It necessitates a thorough understanding of food labels and ingredient lists, as hidden gluten sources can easily be overlooked. This can be challenging when dining out or preparing meals away from home. Furthermore, the diet can be restrictive, potentially limiting access to certain foods and social events.
A well-planned gluten-free diet, however, can be beneficial for individuals with celiac disease, non-celiac gluten sensitivity, or those simply looking to reduce their gluten intake. This dietary shift requires vigilance and a commitment to understanding the nuances of gluten-free products and their potential nutritional trade-offs.
Identifying Hidden Gluten Sources
Navigating the world of gluten-free eating requires a keen awareness of hidden gluten sources. Cross-contamination in food preparation is a significant concern, and it is essential to be aware of how gluten can be introduced unintentionally during cooking or meal preparation. Many processed foods contain hidden gluten, and careful scrutiny of ingredient lists is paramount. This is especially important when eating at restaurants or using shared cooking equipment.
Nutritional Considerations in a Gluten-Free Diet
A gluten-free diet presents potential nutritional challenges, particularly if not carefully planned. Replacing traditional wheat-based foods with gluten-free alternatives requires thoughtful consideration of nutrient content and potential deficiencies. Careful attention must be given to ensuring adequate intake of essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which may be lower in some gluten-free products.
Substituting grains and other foods with gluten-free options might require a careful balancing act to maintain a healthy and balanced diet. Consult with a registered dietitian or nutritionist to ensure that your gluten-free diet provides all the necessary nutrients for optimal health.
The Role of Celiac Disease in Gluten Sensitivity
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten consumption. This immune response causes damage to the small intestine, affecting nutrient absorption and overall health. Celiac disease is a serious condition that requires a lifelong gluten-free diet to manage effectively. Understanding the specific symptoms and complications of celiac disease is vital for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Beyond Celiac: Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity
Non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS) is a condition characterized by symptoms similar to those of celiac disease, but without the same level of intestinal damage. Symptoms can vary widely and often mimic other digestive issues, making diagnosis challenging. While not as severe as celiac disease, NCGS can still significantly impact quality of life and require careful dietary management.
Living a Healthy Life Gluten-Free
Successfully navigating a gluten-free lifestyle requires commitment, education, and a supportive network. Connecting with others who understand the challenges and benefits of this approach can provide valuable guidance and motivation. Finding gluten-free alternatives that meet individual dietary needs and preferences is essential for long-term adherence and enjoyment. Seeking professional guidance from healthcare providers, registered dietitians, and support groups can help individuals successfully navigate the complexities of gluten-free living.

Beyond the Basics: Exploring Innovative Ingredients and Techniques
Beyond Traditional Methods: Utilizing Novel Protein Sources
The culinary world is constantly evolving, and innovative chefs are pushing boundaries by exploring diverse protein sources beyond the conventional meats and poultry. This exploration extends beyond simply substituting existing ingredients; it delves into the unique textural, flavor, and nutritional profiles each offers. For instance, insects, often overlooked in many cultures, are emerging as a sustainable and surprisingly delicious protein option. Their nutritional density and low environmental impact make them a promising ingredient for future culinary innovation.
Plant-based proteins, such as pea protein and soy protein, are also gaining popularity, offering a viable alternative to animal-based proteins for individuals with dietary restrictions or those seeking more sustainable options. The versatility of these plant-based proteins allows for creative applications in various dishes, from meat substitutes to innovative sauces and dressings.
Harnessing the Power of Fermentation
Fermentation, a time-honored culinary technique, is experiencing a resurgence in popularity. This ancient process not only enhances the flavor complexity of ingredients but also contributes to their preservation and nutritional value. Fermented foods, like kimchi, sauerkraut, and kombucha, offer unique tangy and savory notes, adding depth and dimension to culinary creations.
The process of fermentation introduces beneficial microorganisms, which can improve digestion and boost the immune system. This process also contributes to the development of complex flavors and aromas that elevate the overall sensory experience of the dish.
Exploring Molecular Gastronomy Techniques
Molecular gastronomy, a relatively new field, is revolutionizing the way chefs approach food preparation and presentation. Techniques like spherification, emulsification, and foams allow for the creation of visually stunning and texturally exciting dishes. Spherification, for example, creates edible spheres from liquids, enabling chefs to manipulate the mouthfeel and presentation of their creations in innovative ways.
The Science of Texture: Understanding and Manipulating Mouthfeel
The texture of food plays a crucial role in the overall dining experience. Understanding the science behind different textures, from the crispness of a vegetable to the melt-in-your-mouth sensation of a perfectly cooked protein, allows chefs to manipulate these elements to create a symphony of sensations for the palate. This understanding involves exploring how different cooking methods, ingredient combinations, and molecular interactions influence the final texture of a dish.
By understanding the science of texture, chefs can create dishes that not only delight the eyes and nose but also deliver a powerful and memorable sensory experience to the diner. Techniques like sous vide cooking, for example, allow for precise control over the internal temperature of food, leading to exceptionally tender and consistent results.
The Role of Seasonality and Local Sourcing
The use of seasonal ingredients, sourced locally whenever possible, is gaining traction in the culinary world. This approach not only reduces the environmental impact of food production but also allows chefs to showcase the best flavors and textures of the region. By utilizing ingredients at their peak ripeness, chefs can achieve optimal taste and nutritional value.
Local sourcing fosters stronger connections between producers and consumers, supporting local economies and promoting sustainable agricultural practices. This approach also reduces the carbon footprint associated with food transportation, further enhancing the environmental benefits of choosing seasonal and locally sourced ingredients.
Nutritional Considerations in Modern Cuisine
With increasing awareness of the importance of balanced nutrition, chefs are incorporating nutritional factors into their creative culinary endeavors. This involves understanding the nutritional content of different ingredients and how these elements interact within a dish. For example, chefs might focus on creating dishes that provide a good balance of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats, tailoring the nutritional profile to the specific needs of their clientele.
Incorporating superfoods, foods rich in vitamins and minerals, into dishes can further enhance the nutritional value of a meal without compromising flavor or presentation. This sophisticated approach to culinary creation recognizes the interconnectedness of taste, health, and well-being.











