Promoting Environmental Sustainability and Health
Enhancing Local Food Systems
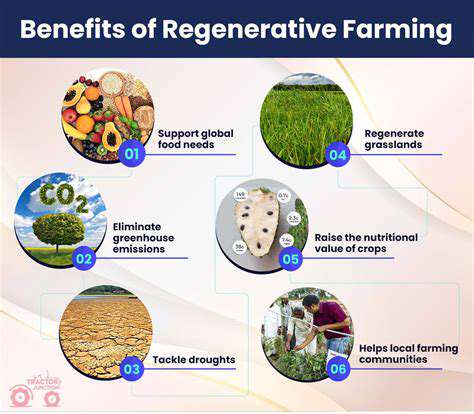
Promoting environmental sustainability and health requires a shift towards more localized food systems. These systems prioritize the production and consumption of food within a defined geographic area. This approach reduces the environmental footprint associated with long-distance transportation of produce, minimizing the carbon emissions and resource depletion that accompany large-scale, industrial agriculture. By supporting local farmers, consumers directly contribute to a more resilient and sustainable food supply chain.
Local food systems empower communities by fostering economic development within their regions. Supporting local farms and businesses creates jobs and strengthens regional economies. This localized approach can also build a stronger sense of community and support local knowledge and expertise in agriculture.
Reducing Environmental Impact
A key benefit of local food systems is their reduced environmental impact. Transporting food over long distances consumes significant amounts of fuel, releasing greenhouse gases into the atmosphere and contributing to climate change. Choosing locally sourced produce minimizes this carbon footprint, fostering a more sustainable food supply. Moreover, local farms often employ more sustainable agricultural practices, such as using less fertilizer and pesticides, which further contributes to environmental health.
Improving Food Quality and Safety
Local food systems often prioritize the quality and safety of food. Farmers who work within a defined region have a closer connection with their customers and can often better regulate the production process, ensuring fresher produce and minimizing the risk of contamination. Consumers also benefit from greater transparency in food sourcing, allowing them to make informed decisions about the food they consume and the farmers who produce it.
Supporting Local Farmers and Communities
Supporting local food systems means directly supporting local farmers and their communities. By purchasing directly from local farms, consumers are able to strengthen the local agricultural economy and create a more resilient food system. This economic support empowers farmers to adopt sustainable practices, invest in their land, and provide for their families. This direct connection also fosters a stronger sense of community and trust between producers and consumers.
Promoting Healthier Diets
Local food systems can play a significant role in promoting healthier diets. By making fresh, locally grown produce more accessible and affordable, these systems encourage consumption of fruits, vegetables, and other nutrient-rich foods. This access to fresher produce often leads to healthier eating habits and a reduction in the consumption of processed foods and those with high levels of sodium and unhealthy fats. This approach also increases consumer awareness of the nutritional value of different foods.
Building Community Bonds and Social Capital
Cultivating Trust and Reciprocity
Building strong community bonds hinges on fostering trust and reciprocity. Local food systems, by their very nature, often involve direct interactions between producers and consumers. These interactions, whether at farmers' markets, community gardens, or through local food cooperatives, provide opportunities for individuals to connect on a personal level, sharing stories, experiences, and even a shared passion for fresh, healthy food. This exchange of information and support builds a foundation of trust within the community, which can be leveraged for other collaborative endeavors.
Furthermore, the act of giving back and supporting local farmers, artisans, and businesses through purchasing local products creates a sense of reciprocity. This exchange of support strengthens the social fabric of the community, fostering a feeling of interdependence and shared responsibility.
Enhancing Social Cohesion
The shared experience of participating in local food systems often leads to a heightened sense of social cohesion. Whether through collaborative community gardening initiatives, food sharing programs, or volunteering at local farms, individuals find common ground and a sense of belonging. These shared activities transcend differences in background, age, or social status, fostering a more unified and supportive community.
Promoting Civic Engagement
Local food systems frequently involve community initiatives, such as farmers' markets, food banks, or community gardens. These initiatives provide opportunities for active civic engagement, encouraging residents to participate in decision-making processes related to their food supply and the well-being of their community. By volunteering or taking on leadership roles in these organizations, individuals develop a sense of ownership and responsibility for the local food system, thereby strengthening their civic engagement.
This involvement in local food systems often extends to advocating for policies that support sustainable and equitable food practices, further strengthening the community's voice in shaping its future.
Strengthening Social Networks
Local food systems act as a catalyst for building and strengthening social networks. Farmers' markets, for example, provide a regular meeting place for people to connect with one another, fostering friendships, and creating opportunities for collaboration. Community gardens, likewise, offer a space for neighbors to interact, share knowledge, and develop a sense of community spirit. These interactions extend beyond the immediate circle, leading to the formation of broader social networks that can benefit the community as a whole.
Creating Shared Values and Identity
The shared experience of producing, consuming, and advocating for local food systems often leads to the development of shared values and a stronger sense of community identity. Participating in these initiatives reinforces a collective commitment to sustainable practices, healthy eating, and supporting local businesses. This shared commitment fosters a sense of belonging and pride in the community, contributing to a more cohesive and resilient social fabric.
Fostering Intergenerational Connections
Local food systems offer unique opportunities for intergenerational connections. Community gardens and farms can bring together people of all ages, fostering shared experiences and knowledge transfer. Children can learn about where food comes from, while older generations can share their wisdom and experiences with younger members of the community. These intergenerational interactions create a sense of continuity and shared history, strengthening the bonds within the community.
Improving Community Health and Wellbeing
Local food systems contribute to the overall health and well-being of a community in several ways. Access to fresh, locally grown produce can improve dietary habits and public health, potentially reducing rates of chronic diseases. The social connections fostered through these systems create a sense of belonging and support, contributing to mental well-being. Moreover, the shared commitment to sustainable practices fosters a sense of collective responsibility for the community's health and well-being.