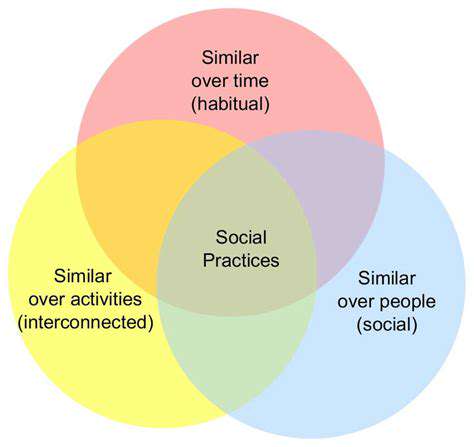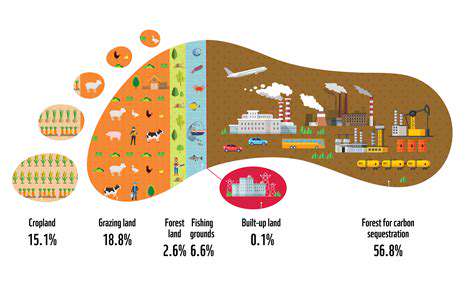
Defining Environmental Sustainability
Modern environmental sustainability goes beyond simple conservation efforts. It represents a comprehensive strategy for managing resources while ensuring ecological balance. The core principle involves meeting current human needs without jeopardizing future generations' ability to meet theirs. This paradigm shift demands fundamental changes in how we value and consume resources, moving from wasteful practices to thoughtful utilization. Understanding the delicate balance within ecosystems is equally vital for achieving true sustainability.
What makes sustainability particularly challenging is recognizing how environmental factors intertwine with social and economic aspects. Effective sustainable solutions must account for their long-term effects on communities, businesses, and natural systems simultaneously. Only through this integrated approach can we develop solutions that endure.
Measuring Environmental Impact
To gauge our progress toward sustainability, we need robust methods for evaluating environmental effects. Scientists have developed various metrics that track different forms of ecological damage, from carbon emissions to habitat destruction. Without precise measurement tools and consistent data gathering, we can't make informed policy decisions or track improvement accurately.
The field offers multiple assessment techniques, each with specific applications. Life-cycle analysis examines products from creation to disposal, while ecological footprint calculations measure resource consumption. Applying these methods systematically helps identify where changes can make the most significant difference in reducing environmental harm.
Indicators of Environmental Health
Environmental health can be monitored through numerous measurable indicators. These include but aren't limited to air purity measurements, water quality tests, and biodiversity surveys. Regular tracking of these markers allows scientists to detect negative trends early and implement corrective measures before problems escalate.
The information gathered from these indicators serves another crucial purpose. By analyzing the data, researchers can evaluate whether current environmental policies yield positive results. This feedback loop enables continuous refinement of conservation strategies for better outcomes.
Economic Valuation of Ecosystem Services
Nature provides countless services that sustain human life and economic activity, yet their value often goes unrecognized in financial systems. Clean water, crop pollination, and climate regulation all have substantial economic worth that should factor into decision-making processes.
Economists have devised several approaches to quantify these benefits. Techniques like contingent valuation and cost-benefit analysis help demonstrate the financial wisdom of protecting natural systems. When decision-makers understand the economic stakes, they're more likely to prioritize environmental protection in their policies.
Sustainability Reporting and Accountability
For sustainability efforts to be effective, organizations must maintain transparency about their environmental performance. Detailed reporting on emissions, resource use, and waste management allows stakeholders to assess corporate responsibility.
Standardized reporting frameworks ensure that environmental data remains comparable across industries and time periods. More rigorous accountability standards would encourage businesses to continuously improve their environmental performance rather than settle for minimum compliance.
Beyond Calories: Highlighting Health Benefits and Functional Foods

Beyond the Calorie Count: Understanding Macronutrients
The calorie-centric view of nutrition oversimplifies the complex relationship between food and health. Macronutrients - proteins, carbohydrates, and fats - each play distinct and vital roles in bodily functions. Grasping how these nutrients interact within our bodies provides the foundation for lasting health and effective weight management. Proteins rebuild tissues, carbohydrates fuel our activities, and fats support critical biological processes often overlooked in popular diet culture.
Nutrient quality matters as much as quantity. Highly processed foods may be calorie-controlled but often lack nutritional value, potentially leading to metabolic issues despite meeting energy needs. In contrast, whole foods rich in diverse nutrients promote satiety and metabolic health regardless of calorie density.
The Importance of Micronutrients: Supporting Cellular Function
While macronutrients get most attention, micronutrients - vitamins and minerals - serve as essential cofactors in countless biochemical reactions. Their absence, even in small amounts, can disrupt entire physiological systems. The human body operates like a complex machine requiring all its micronutrient parts to function optimally.
This explains why nutritionists emphasize varied, colorful diets. Different plant foods contain unique micronutrient profiles, making dietary diversity the best insurance against deficiencies. A rainbow plate isn't just aesthetically pleasing - it's biochemically strategic.
The Role of Hydration and Gut Health: Supporting a Healthy Metabolism
Water's importance extends far beyond quenching thirst. This fundamental nutrient facilitates nutrient transport, temperature regulation, and waste removal. Optimal hydration creates the fluid environment where all metabolic processes can occur efficiently. Proper water intake also helps regulate appetite signals, supporting natural weight management.
The gut microbiome represents another crucial metabolic factor. This complex bacterial ecosystem influences everything from nutrient absorption to immune response. Feeding these beneficial microbes with fiber-rich and fermented foods creates a symbiotic relationship that enhances overall health.
Personalized and Interactive Food Labels: The Future is Digital

Tailored Culinary Experiences
The food industry is evolving toward hyper-personalization, recognizing that one-size-fits-all approaches fail to meet diverse consumer needs. Modern solutions allow customization that considers individual health profiles, taste preferences, and lifestyle factors. This personal touch increases engagement with healthy eating habits by making them feel specifically designed rather than imposed. Digital platforms amplify this trend by collecting user data to generate bespoke recommendations.
Interactive food experiences add an engaging dimension to eating. Whether through augmented reality labels or virtual cooking sessions, these innovations transform passive consumption into active participation. The educational value of these interactions often leads to lasting changes in food choices and preparation habits. When people understand and engage with their food at this level, they develop deeper appreciation for quality ingredients and culinary traditions.
Enhanced Nutritional Value and Health Benefits
Personalized nutrition takes generic dietary advice and makes it relevant to individuals. By analyzing personal health metrics and goals, these systems can recommend foods that specifically address nutritional gaps or health concerns. This targeted approach gives people tangible tools to take charge of their wellbeing through food choices.
Interactive platforms excel at nutritional education. Through engaging formats like gamification or virtual demonstrations, they can illustrate how different foods affect the body or how cooking methods alter nutritional profiles. This knowledge transfer empowers more conscious eating decisions grounded in scientific understanding rather than trends.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
The democratization of personalized nutrition represents significant progress in food equity. Advanced systems now accommodate various dietary restrictions, cultural preferences, and budget considerations. Breaking down these barriers ensures that nutritional optimization isn't limited to privileged groups but available to all.
Interactive food technology also builds cultural bridges. Shared virtual cooking experiences can introduce participants to global cuisines and traditions they might otherwise never encounter. This digital culinary diplomacy fosters cross-cultural appreciation through the universal language of food.