The Interplay Between Diet and Thyroid Health
The Role of Nutrients in Thyroid Function
Maintaining a well-rounded diet is fundamental for proper thyroid function. Key minerals including iodine, selenium, zinc, and iron play instrumental roles in both producing and regulating thyroid hormones. Iodine stands out as particularly critical since it serves as the foundation for thyroid hormone creation, with shortages potentially triggering hypothyroidism. Regularly eating iodine-packed foods—think seafood, iodized salt, and select produce—helps sustain normal thyroid operations. Additionally, getting enough selenium proves necessary for enzymes that process thyroid hormones, facilitating their effective conversion and bodily use.
The general nutritional quality of one's diet also heavily influences thyroid well-being. Antioxidant-loaded fruits and vegetables can shield thyroid cells from oxidative damage, which frequently accompanies thyroid issues. Meals containing lean proteins, complex carbs, and beneficial fats deliver steady energy while aiding metabolic functions governed by thyroid hormones. Proper hydration likewise remains vital for hormone transportation and cellular activities. Emphasizing whole, minimally processed foods while cutting back on refined sugars and unhealthy fats typically benefits thyroid health most.
Dietary Strategies for Thyroid Management
Strategic eating approaches can effectively help control thyroid disorders. Those with underactive thyroids might focus on easily processed proteins, good fats, and complex carbohydrates to bolster energy and wellness. Rather than obsessing over calories, prioritizing nutrient-rich foods ensures the body obtains crucial vitamins and minerals. Certain dietary tweaks—like boosting fiber for better digestion or eating more iron-rich items to address deficiencies—can alleviate hypothyroid symptoms. Collaborating with healthcare experts allows for creating tailored meal plans addressing individual health circumstances.
For overactive thyroid conditions, dietary changes may help manage issues like nervousness, weight loss, and rapid heartbeat. Sticking to whole foods while avoiding processed items, refined sugars, and too much caffeine could help stabilize metabolism and ease symptoms. While diet alone won't cure thyroid problems, combining nutritional adjustments with medical treatment often yields the best outcomes. Endocrinologists can design comprehensive management approaches incorporating both dietary and clinical interventions.

Dietary Strategies for Hyperthyroidism
Understanding Hyperthyroidism
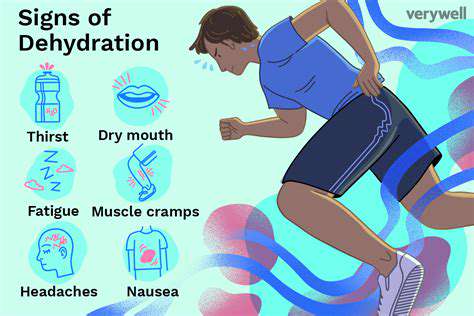
Hyperthyroidism involves excessive thyroid hormone production, disrupting numerous bodily processes and generating symptoms ranging from mild to intense. Accurately identifying these manifestations and their biological underpinnings proves essential for proper treatment. Many people notice signs like anxiety, restlessness, and heart palpitations early on, making prompt recognition important.
Dietary Considerations for Thyroid Function
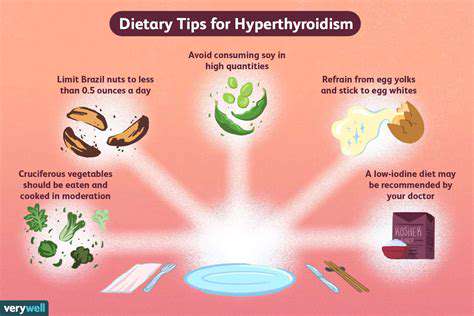
Nutrition significantly impacts thyroid performance. Consuming diverse, nutrient-packed foods helps maintain thyroid equilibrium. While incorporating iodine sources like seafood and iodized salt matters, avoiding overconsumption remains equally important. The diet should also supply ample selenium and zinc, both indispensable for hormone creation.
Importance of Iodine Intake
Iodine serves as the primary building block for thyroid hormones. Inadequate iodine levels can impair thyroid operations, possibly resulting in hypothyroidism or related conditions. Beyond iodized salt, diverse dietary sources—including dairy and certain plants—help meet daily iodine requirements.
Managing Carbohydrate Intake
While carbohydrates provide essential energy, their quality and quantity affect thyroid health. Choosing complex over simple carbohydrates helps stabilize blood sugar, indirectly supporting thyroid operations. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables offer these beneficial carbs alongside other valuable nutrients.
Protein and Nutrient Intake
Proteins contribute significantly to hormone production processes. Adequate protein consumption proves critical for generating thyroid hormones and sustaining general well-being. Lean options like poultry, fish, legumes, and lentils supply necessary amino acids while helping with satiety and weight control—common concerns with thyroid issues.
Hydration and Overall Diet
Proper fluid intake remains crucial, especially for hyperthyroid individuals. Sufficient water consumption aids nutrient uptake and toxin elimination while potentially easing symptoms. A varied diet featuring produce, whole grains, and lean proteins supports both thyroid function and comprehensive health management.