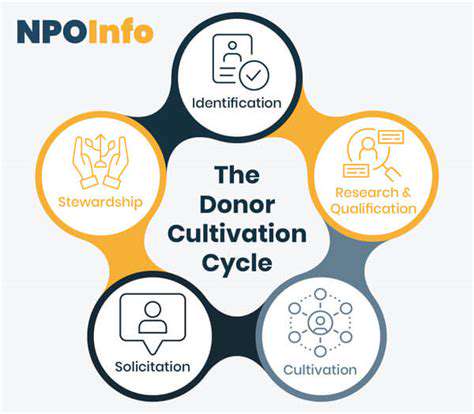
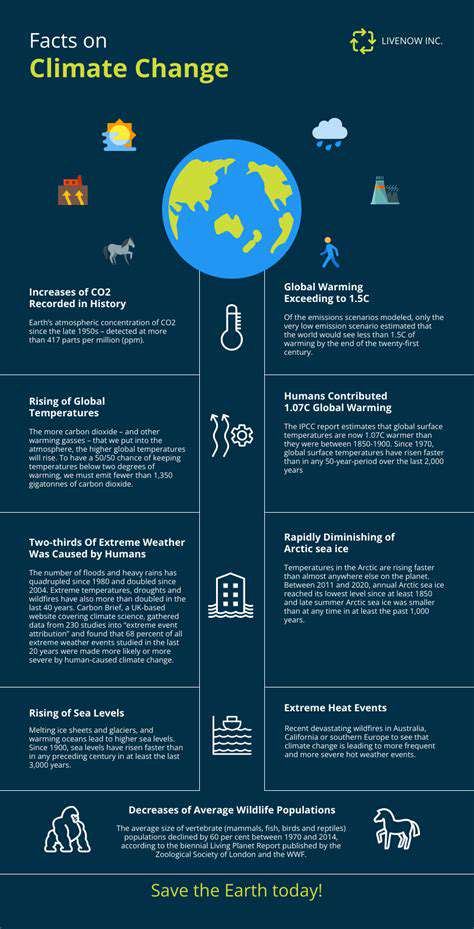
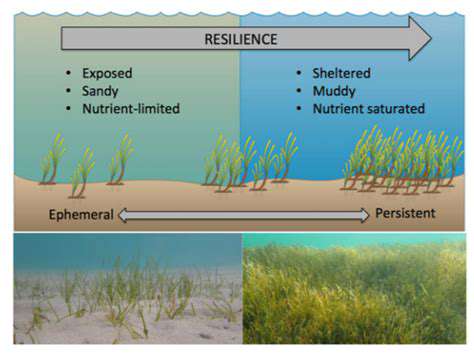
The integration of technology into healthcare is revolutionizing the industry, from remote patient monitoring to telehealth consultations. Digital health tools are enabling more accessible and personalized care, breaking down geographical barriers and potentially improving patient outcomes. This shift is particularly significant for underserved populations, who may now have easier access to specialists and vital resources.
The Economic Implications of Food Waste
The Financial Burden of Food Waste
Food waste, a pervasive issue across the globe, imposes substantial financial burdens on individuals, households, and businesses. The costs associated with wasted food extend beyond the initial purchase price. These include the expenses involved in growing, processing, transporting, and storing the food that ultimately ends up in landfills. These resources could be diverted to produce food that is actually consumed, thereby reducing the overall financial strain on the food system.
Furthermore, the disposal of food waste contributes to the expenses associated with waste management infrastructure, including landfill maintenance and environmental cleanup. The financial burden of food waste reverberates throughout the supply chain, impacting farmers, processors, retailers, and consumers alike.
Environmental Impact of Food Waste
The environmental impact of food waste is significant and far-reaching. Massive amounts of resources, including water, land, and energy, are used in the production of food that is never consumed. This contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution. The decomposition of food waste in landfills releases harmful greenhouse gases, exacerbating climate change. Reducing food waste is crucial for mitigating these environmental consequences.
Food Waste and Resource Depletion
The production of food demands a considerable amount of resources. From the water used in irrigation to the energy required for transportation and processing, the resources consumed in producing food that is ultimately wasted are substantial. This resource depletion has a direct impact on the availability of resources for other essential needs. Reducing food waste helps conserve these precious resources for future generations.
The Social Cost of Food Waste
Beyond the economic and environmental consequences, food waste carries a significant social cost. In many parts of the world, food insecurity is a pressing issue. Vast quantities of perfectly edible food are discarded while millions lack access to nutritious food. This disparity highlights the ethical implications of food waste and underscores the need for solutions to address both the waste and the lack of access.
The Impact on Agricultural Practices
Food waste significantly impacts agricultural practices. The production of food destined for waste consumes valuable land, water, and labor, thereby reducing the overall efficiency of agricultural systems. This inefficiency can affect the profitability of farms and the overall sustainability of food production. Optimizing food systems to reduce waste is essential for the long-term viability of agricultural practices.
Consumer Behavior and Food Waste
Consumer behavior plays a pivotal role in the food waste problem. Inadequate storage, improper handling, and miscalculations in portion sizes contribute significantly to food waste at the household level. Educating consumers about proper food storage, meal planning, and portion control can drastically reduce food waste. Promoting mindful consumption habits is crucial in mitigating the problem.
Waste Reduction Strategies and Economic Benefits
Implementing effective waste reduction strategies can yield significant economic benefits. These strategies include improved food storage techniques, precise inventory management, and the development of innovative food preservation methods. By reducing food waste, businesses can lower costs, increase efficiency, and contribute to a more sustainable food system. This also creates opportunities for economic growth in related sectors, such as composting and food rescue programs.