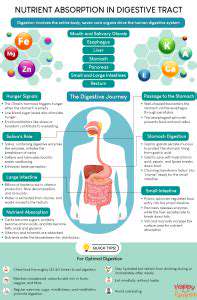
Understanding the Connection Between Diet and Hormones
Personalized nutrition plays a crucial role in achieving hormonal balance because the foods we consume directly impact hormone production and regulation. Different nutrients are essential for various hormonal processes, from thyroid function to insulin sensitivity. Understanding these intricate relationships allows for targeted dietary interventions to support optimal hormonal health and address potential imbalances.
A balanced diet rich in whole foods, vitamins, and minerals, tailored to individual needs and preferences, can significantly impact hormonal health. Conversely, a diet lacking in essential nutrients or excessive in processed foods and unhealthy fats can disrupt hormonal equilibrium, potentially leading to a cascade of health issues.
The Role of Macronutrients in Hormonal Regulation
Macronutrients like protein, carbohydrates, and fats all have unique impacts on various hormones. Protein, for instance, is essential for building and repairing tissues, and is involved in the production of hormones like insulin and growth hormone. A balanced intake of protein can support healthy hormone levels, while inadequate protein intake may lead to hormonal imbalances.
Carbohydrates are another crucial macronutrient. Complex carbohydrates provide sustained energy and are important for regulating blood sugar, which directly influences insulin and other hormones. However, excessive consumption of refined carbohydrates can disrupt blood sugar control and impact hormone balance.
The Importance of Micronutrients for Hormone Production
Micronutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, are essential cofactors in numerous hormonal processes. For example, vitamin D plays a critical role in calcium absorption, which is vital for hormone production and regulation. Inadequate intake of specific vitamins and minerals can lead to hormonal imbalances and related health issues.
Personalized Dietary Strategies for Hormonal Balance
Personalized dietary strategies for hormonal balance take into account individual factors such as age, activity level, medical history, and specific hormonal needs. A qualified nutritionist or healthcare professional can help design a personalized dietary plan to address individual hormonal imbalances and support overall health.
This approach considers specific needs, such as dietary restrictions, allergies, and preferences, to create a sustainable and enjoyable plan. This tailored approach ensures that the dietary strategy is not only effective but also practical and maintainable.
Addressing Specific Hormonal Imbalances Through Diet
Dietary interventions can be tailored to address specific hormonal imbalances. For example, a diet rich in phytoestrogens, found in soy products and other plant-based foods, may help regulate estrogen levels in women. Similarly, a diet rich in zinc, found in various foods like oysters and pumpkin seeds, can support testosterone production in men.
Monitoring Progress and Making Adjustments
Regular monitoring of progress is crucial in personalized nutrition for hormonal balance. This involves tracking symptoms, blood tests, and overall well-being to assess the effectiveness of the dietary plan. Based on the results, necessary adjustments can be made to optimize the plan and ensure ongoing support for hormonal health.
Continuous communication with healthcare professionals ensures that the dietary plan remains aligned with individual needs and that any potential complications are addressed promptly. This dynamic approach to personalized nutrition allows for flexibility and adaptation as hormonal needs change over time.
Dietary Strategies for Hormonal Balance

Nutrient Timing for Hormone Regulation
Understanding the timing of nutrient intake can significantly impact hormone balance. Consuming a balanced breakfast rich in protein and complex carbohydrates can help regulate blood sugar levels, preventing spikes and crashes that can disrupt insulin and other hormone pathways. This balanced approach can also contribute to sustained energy throughout the day, reducing cravings and improving overall mood. A consistent meal schedule, even on non-workout days, can aid in stabilizing hormones and maintaining metabolic function.
Eating a protein-rich lunch can support healthy hormone production. Protein is essential for hormone synthesis and repair, playing a key role in the production of hormones like testosterone and estrogen. Including healthy fats in your meals, especially in your lunch, can help regulate hormones and promote satiety, preventing overeating and subsequent hormonal imbalances. Prioritizing whole foods over processed options is crucial for optimal nutrient absorption and hormonal health.
The Impact of Macronutrients on Hormonal Health
Macronutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, play a vital role in hormone regulation. A diet rich in complex carbohydrates provides sustained energy and supports healthy blood sugar levels, which are critical for hormonal balance. These types of carbs are found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Incorporating lean protein sources, such as fish, poultry, and beans, is essential for hormone synthesis and repair. Sufficient protein intake is essential for creating and maintaining hormones that control everything from metabolism to mood.
Healthy fats, like those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, are crucial for hormone production and function. These fats are essential components of hormone structures, supporting the production and regulation of many hormones in the body. A diet lacking in healthy fats can lead to hormonal imbalances, affecting everything from mood to energy levels.
Fiber's Role in Hormonal Balance
Dietary fiber is an often-overlooked component of a healthy diet for hormonal balance. Soluble fiber, found in oats, beans, and fruits, helps regulate blood sugar levels and promotes satiety. This regulation of blood sugar is essential for preventing hormonal fluctuations and maintaining a stable hormonal environment.
Insoluble fiber, found in vegetables, promotes healthy digestion, which is crucial for nutrient absorption and overall well-being. A diet rich in fiber can contribute to weight management, reducing inflammation, and supporting the health of the gut microbiome, a critical factor in hormonal balance. A healthy gut microbiome is vital for the production of numerous hormones and neurotransmitters.
Hydration and Hormonal Health
Adequate hydration is essential for optimal hormone function. Water is vital for transporting hormones throughout the body and supporting various metabolic processes. Dehydration can lead to hormonal imbalances and disrupt the delicate balance of hormones. Staying properly hydrated is crucial for maintaining energy levels, regulating mood, and supporting overall health.
Drinking sufficient water throughout the day helps with many bodily functions, including hormone regulation. It supports various metabolic processes which also contribute to better hormone regulation. Pay attention to your body's signals for thirst and adjust your water intake accordingly.
Addressing Stress and its Impact on Hormones
Chronic stress significantly impacts hormonal balance. Stress hormones like cortisol, when elevated for extended periods, can disrupt other hormone systems, potentially leading to a cascade of negative effects on health. Managing stress through techniques like exercise, meditation, or mindfulness can help regulate cortisol levels and maintain hormonal balance.
Furthermore, stress can affect sleep quality, which is inextricably linked to hormonal health. Good sleep is essential for hormone production and regulation. Insufficient sleep can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance, leading to various health issues. Prioritizing stress reduction and adequate sleep is critical for maintaining hormonal well-being.
The Role of Micronutrients in Hormonal Health

Essential Micronutrients for Hormonal Balance
Micronutrients, though present in smaller amounts compared to macronutrients, play a crucial role in various bodily functions, including hormone production and regulation. These essential vitamins and minerals act as cofactors in enzymatic reactions that are vital for hormone synthesis, transport, and receptor activity. A deficiency in even one micronutrient can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance, leading to a cascade of health issues. Understanding the importance of these micronutrients is key to maintaining optimal hormonal health and overall well-being.
For instance, vitamin D, often overlooked, is critical for calcium absorption and plays a vital role in regulating various hormones. Adequate intake of vitamin D is essential for ensuring optimal calcium levels, which are crucial for hormonal signaling.
Zinc and its Hormonal Impact
Zinc is a vital trace mineral that plays a multifaceted role in hormonal health. It's involved in the synthesis and function of numerous hormones, including insulin, testosterone, and thyroid hormones. Zinc deficiency can lead to impaired hormone production and disrupt the overall hormonal equilibrium. This can manifest in various ways, affecting mood, energy levels, and even reproductive health.
Furthermore, zinc is crucial for the proper functioning of the immune system, which is also intricately linked to hormonal balance. A strong immune system helps to maintain homeostasis and ensure the proper functioning of hormonal pathways.
The Role of Vitamin B in Hormone Production
Several B vitamins are crucial for hormone production. These water-soluble vitamins act as coenzymes in various metabolic pathways, including those involved in hormone synthesis. Vitamin B deficiencies can lead to hormonal imbalances, impacting energy levels, mood, and overall health. For example, vitamin B6 is involved in the conversion of tryptophan to serotonin, a crucial neurotransmitter that impacts mood and sleep cycles, which are heavily influenced by hormonal activity.
Moreover, adequate levels of B vitamins are also essential for proper thyroid function, a gland that plays a vital role in regulating metabolism and influencing the action of other hormones.
Iron and its Impact on Hormonal Health
Iron, while often associated with red blood cell production, also plays a surprising role in hormonal health. It's crucial for the production of hormones like estrogen and testosterone. Iron deficiency can directly impact hormone production and can result in a cascade of hormonal imbalances affecting various bodily functions. Iron deficiency can negatively impact both men and women's hormonal health.
Furthermore, iron is integral to cellular energy production, which is critical for the function of endocrine glands and the various hormonal pathways throughout the body.
Iodine and Thyroid Function
Iodine is an essential mineral that is vital for the production of thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism, growth, and development. An iodine deficiency can lead to hypothyroidism, characterized by a sluggish metabolism and a range of other health issues. Ensuring adequate iodine intake is crucial for maintaining optimal thyroid function, which directly impacts the overall hormonal balance.
Iodine deficiency is a preventable cause of hormonal disruption. A balanced diet that includes iodine-rich foods, or a supplement as prescribed by a healthcare professional, can help maintain optimal thyroid function and overall hormonal health.
One of the key characteristics of almond flour is its texture. Unlike traditional wheat flour, it results in a denser, chewier, and often slightly sweeter baked product. This is due to its unique fat content and protein makeup. This different texture can be a game-changer for those seeking to elevate their baking. Knowing how to adjust recipes accordingly is key to achieving the desired outcome.
Monitoring Progress and Adapting the Plan
Tracking Key Metrics
A crucial aspect of personalized nutrition for hormone balance is meticulously tracking key metrics. This allows for ongoing assessment of the effectiveness of the chosen dietary plan and enables necessary adjustments. Monitoring parameters such as weight, body composition (using tools like calipers or DEXA scans), energy levels, sleep quality, mood, and menstrual cycle regularity (for women) provides valuable insights into how the personalized nutrition plan is impacting the body's hormonal system. This data-driven approach ensures that the plan remains aligned with individual needs and goals, ensuring the most optimal results possible.
Regular blood tests, particularly those assessing hormone levels (like testosterone, estrogen, cortisol, and thyroid hormones), are essential for understanding the impact of dietary changes. These tests, performed in conjunction with tracking other metrics, offer a comprehensive view of the body's response to the personalized nutrition plan and allow for prompt adjustments if necessary. Consistent monitoring empowers both the individual and the healthcare professional to tailor the plan for optimal results, fostering a dynamic and responsive approach to achieving hormone balance.
Adapting the Plan Based on Results
The personalized nature of the nutrition plan hinges on its adaptability. Regular evaluation of the tracked metrics is crucial for making necessary adjustments. If a certain food item or dietary pattern isn't producing the desired hormonal response, it might be necessary to modify it or completely remove it from the plan. This iterative process, based on observed results, ensures that the plan evolves with the individual's unique body and response.
For example, if someone notices increased anxiety and irritability after consuming a particular type of carbohydrate, the plan should be adjusted to include alternative sources of carbohydrates or reduce the portion size. This responsiveness to individual needs is paramount in achieving sustainable hormonal balance. It is important to remember that the plan is a living document, not a rigid set of rules, and should be adjusted based on ongoing evaluation and feedback from the body.
Addressing Challenges and Roadblocks
Implementing a personalized nutrition plan for hormone balance may present unforeseen challenges. For instance, some individuals might struggle with adherence to the dietary guidelines, feeling overwhelmed by the changes or experiencing cravings for prohibited foods. Addressing these challenges proactively is essential for long-term success. Strategies for overcoming these obstacles could include seeking support from a registered dietitian or a nutrition coach, using meal prepping techniques to simplify food preparation, or gradually introducing dietary modifications to avoid feelings of deprivation.
Other potential roadblocks include unexpected health issues, stress levels, or environmental factors that could impact hormone balance. The plan needs to be flexible enough to accommodate these variables. Open communication with the healthcare professional overseeing the plan is essential to address any emerging concerns or challenges. By understanding and proactively addressing potential roadblocks, individuals can enhance their commitment to the plan and maximize their chances of achieving their hormonal balance goals.