The Gut Microbiome: A Complex Ecosystem
The human gut is teeming with trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiome. This complex ecosystem plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, impacting everything from digestion and nutrient absorption to immune function and even mental well-being. Understanding the intricate workings of this community is essential to appreciating the profound impact of fermented foods on our health.
These microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, interact with each other and with the host in a delicate balance. Disruptions to this balance, often referred to as dysbiosis, can lead to a range of health problems. The specific composition and activity of the gut microbiome are influenced by several factors, including diet, genetics, and environmental exposures.
The Role of Fermented Foods in Gut Microbiome Health
Fermented foods are a key dietary component that can significantly influence the composition and function of the gut microbiome. These foods are created through a controlled fermentation process, which involves the growth of beneficial microorganisms like bacteria and yeasts. These microorganisms break down complex carbohydrates, proteins, and other compounds, creating beneficial byproducts.
Consuming fermented foods provides a prebiotic effect, meaning they serve as a food source for the beneficial bacteria already present in the gut, promoting their growth and activity. This, in turn, fosters a healthier and more balanced gut microbiome.
Fermented Foods: A Source of Prebiotics and Probiotics
Prebiotics are non-digestible food ingredients that selectively stimulate the growth and/or activity of beneficial bacteria in the colon, while probiotics are live microorganisms which, when consumed in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit to the host. Fermented foods are excellent sources of both prebiotics and probiotics.
The fermentation process creates an environment where these beneficial microorganisms thrive, resulting in a rich source of live and active cultures. This can lead to improved digestive health and overall well-being.
The Impact of a Healthy Gut Microbiome on Overall Health
A balanced and diverse gut microbiome has far-reaching implications for overall health. It plays a critical role in supporting immune function, protecting against pathogens, and influencing metabolism. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome can contribute to improved digestion, reduced inflammation, and a stronger defense against various diseases.
Moreover, emerging research suggests a link between a healthy gut microbiome and mental well-being. The gut-brain axis, a complex communication system between the gut and the brain, highlights how the gut microbiome can influence mood and cognitive function. This underscores the importance of fostering a healthy gut microbiome through a balanced diet, including fermented foods.
Specific Examples of Fermented Foods and Their Benefits
Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha are just a few examples of the wide variety of fermented foods available. Each of these foods offers unique benefits based on the specific microorganisms used in the fermentation process. For instance, yogurt is often fortified with probiotics, while sauerkraut provides a rich source of beneficial bacteria.
The variety of fermented foods allows individuals to explore different flavors and textures while simultaneously supporting a healthy gut microbiome. Exploring diverse fermented foods can be an enjoyable and beneficial way to enhance your diet.
Maintaining a Healthy Gut Microbiome: Beyond Fermented Foods
While fermented foods are a powerful tool in promoting a healthy gut microbiome, a holistic approach is crucial. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, along with adequate hydration and stress management, further supports a thriving microbiome. Avoiding excessive consumption of processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats is equally important.
Regular physical activity and sufficient sleep also contribute to overall well-being and a healthy gut microbiome. Implementing these lifestyle choices, combined with the strategic inclusion of fermented foods, can lead to a significant improvement in digestive health and overall well-being.
Digestive Health and Improved Nutrient Absorption
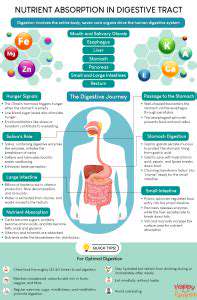
Understanding the Importance of Digestive Health
Digestive health plays a crucial role in overall well-being, impacting everything from nutrient absorption to mood regulation. A healthy digestive system is essential for extracting the vital nutrients from the food we eat, which are then used to fuel our bodies and support various bodily functions. This process of nutrient extraction and absorption is directly linked to our energy levels and overall health.
Furthermore, a balanced digestive system contributes to a strong immune system, as the gut microbiome plays a vital role in immune function. Maintaining a healthy gut environment helps the body fight off infections and diseases more effectively.
The Connection Between Diet and Digestive Function
The foods we consume directly impact the health of our digestive system. A diet rich in fiber-rich fruits, vegetables, and whole grains promotes healthy bowel movements and prevents constipation. A balanced diet with a variety of nutrients is crucial for maintaining a healthy digestive system.
Processed foods, excessive sugar intake, and a lack of fiber can disrupt the delicate balance of the gut microbiome, leading to digestive issues like bloating, gas, and indigestion.
The Role of Probiotics in Digestive Health
Probiotics, beneficial bacteria found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, are essential for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. These beneficial bacteria help to support the growth of good bacteria in the gut, improving digestion and overall gut health.
Consuming probiotic-rich foods can be a valuable strategy for promoting a healthy digestive system and preventing digestive issues.
Managing Stress for Digestive Well-being
Stress can significantly impact digestive health. Chronic stress can lead to digestive issues such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), acid reflux, and other gastrointestinal problems. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and mindfulness practices can help support a healthy digestive system.
Hydration and Digestive Health
Proper hydration is crucial for healthy digestion. Water helps to soften stool and aids in the smooth movement of food through the digestive tract, preventing constipation. Staying properly hydrated can significantly reduce the risk of experiencing digestive problems.
The Importance of Fiber in Digestion
Fiber is essential for promoting healthy digestion. It adds bulk to the stool, stimulating regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Including fiber-rich foods in your diet is vital for maintaining a healthy digestive system and preventing various digestive ailments.
Lifestyle Factors Impacting Digestive Health
Beyond diet and stress management, several lifestyle factors can influence digestive health. Regular exercise promotes healthy digestion, while adequate sleep allows the body to repair and restore itself, supporting optimal digestive function. Engaging in regular physical activity and prioritizing sufficient sleep are pivotal factors for maintaining a healthy digestive system and overall well-being. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also negatively impact digestive health, so limiting these habits can be beneficial.