Polyunsaturated fatty acids, which include omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, are crucial for brain development and function. They are often found in fatty fish, nuts, and seeds.
Health Benefits of Unsaturated Fats
Consuming unsaturated fats, especially omega-3s, can contribute to improved heart health by lowering bad cholesterol levels and increasing good cholesterol. This can reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Furthermore, unsaturated fats are important for brain health and cognitive function. They play a significant role in the structure and function of brain cells, contributing to better memory and focus.
Dietary Sources of Unsaturated Fats
A variety of foods contain unsaturated fatty acids. Healthy fats are found in avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish like salmon and tuna. Including these foods in your diet can provide your body with the essential nutrients it needs.
The Importance of a Balanced Diet
While unsaturated fats are beneficial, it's crucial to remember that a balanced diet encompassing a variety of nutrients is essential for overall health. Excessive consumption of any type of fat, including unsaturated fats, can lead to health issues.
The Impact on Cell Membranes
Unsaturated fatty acids are crucial components of cell membranes. Their flexibility and fluidity are vital for proper cell function, allowing for the efficient transport of nutrients and signaling molecules across the membrane. This flexibility is directly related to their unsaturated nature.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While unsaturated fats are generally considered healthy, some individuals may need to be mindful of their intake. For example, certain conditions, such as high triglycerides, might require a more cautious approach to fat consumption.
It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the appropriate amount of unsaturated fats for individual needs and health conditions.
Oxidative Degradation Products and Their Impact
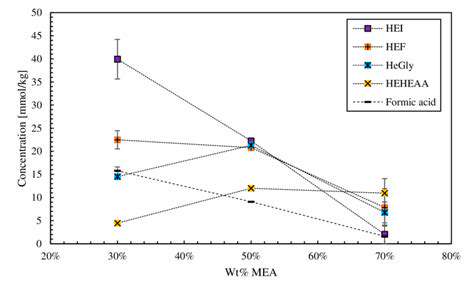
Oxidative Degradation Pathways
Oxidative degradation, a crucial process in various fields, involves the breakdown of molecules by reacting with oxygen. Understanding these pathways is essential for comprehending the mechanisms behind aging and deterioration of materials. This process occurs through a series of reactions, often initiating with the formation of free radicals. These highly reactive species then propagate chain reactions that ultimately lead to the fragmentation and alteration of the original molecule structure.
The specific pathways vary greatly depending on the type of molecule being degraded and the environmental conditions. Factors such as temperature, pH, and the presence of catalysts all play significant roles in influencing the rate and extent of oxidative degradation. These pathways often involve the formation of intermediate products, which can themselves be reactive and contribute to further degradation.
Impact on Material Properties
Oxidative degradation significantly impacts the properties of many materials, leading to deterioration in performance and functionality. For instance, in polymers, oxidative degradation can result in reduced strength, altered color, and embrittlement, rendering the material unusable or less effective over time. This is particularly relevant in the food industry, where oxidation can lead to spoilage and compromised quality.
In biological systems, oxidative degradation plays a crucial role in cellular aging and the development of diseases. Oxidative stress, the imbalance between reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defenses, contributes to damage in cellular components like proteins and DNA, potentially leading to various health issues.
Identification and Analysis Techniques
Identifying and analyzing the products of oxidative degradation is crucial for understanding the mechanisms involved and for developing appropriate preservation strategies. Various analytical techniques are employed, including spectroscopy (UV-Vis, FTIR, NMR) and chromatography (GC, HPLC), to detect and quantify the degradation products. These techniques provide insights into the specific chemical changes occurring during the degradation process.
Advanced techniques, like mass spectrometry, allow for the precise identification of complex mixtures of degradation products, providing valuable information about the reaction pathways and the intermediates involved. This information is critical for developing effective strategies to prevent or mitigate oxidative degradation.
Applications in Various Industries
Oxidative degradation is a critical concern across many industries. In food packaging, preventing oxidation is essential to maintain product quality and safety. In the pharmaceutical industry, understanding oxidative degradation is crucial for preserving drug efficacy and stability. The petroleum industry faces challenges related to the oxidation of fuels and lubricants.
Understanding the mechanisms and products of oxidative degradation is essential for developing advanced materials with improved resistance to oxidation and for designing effective preservation strategies in various sectors. This knowledge facilitates the development of more durable and longer-lasting products and systems.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Various strategies are employed to prevent or mitigate oxidative degradation, depending on the specific application. Antioxidants, often used in food and other products, can scavenge free radicals and inhibit the degradation process. Protective coatings and packaging materials can create a barrier against oxygen and moisture. Controlling environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity is also important to slow down the rate of oxidation.
Developing advanced materials with inherent resistance to oxidative degradation is an active area of research. This involves modifying material structures and incorporating specialized additives to enhance their stability. These strategies are crucial for maintaining the quality and performance of materials over extended periods.
Omega-3 fatty acids, crucial components of a healthy diet, play a significant role in mitigating inflammation throughout the body. These essential fatty acids, primarily found in fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel, as well as flaxseeds and chia seeds, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. They work by influencing the production of eicosanoids, molecules that regulate inflammation. Specifically, omega-3s encourage the production of anti-inflammatory eicosanoids while suppressing the production of pro-inflammatory ones, thus contributing to a reduction in pain and swelling associated with various inflammatory conditions.
Preservation Strategies and Antioxidants
Preservation Strategies for Oils and Fats
Preservation strategies for oils and fats are crucial in mitigating the detrimental effects of oxidation. These strategies aim to slow down or halt the chemical reactions that lead to rancidity and spoilage. A primary focus is on preventing contact with oxygen, light, and heat, as these are key factors driving oxidation. Proper storage conditions, including airtight containers and cool, dark locations, are vital in extending the shelf life of these valuable ingredients.
Innovative packaging technologies, such as modified atmosphere packaging (MAP), are also employed to reduce exposure to oxygen. These techniques involve altering the gas composition surrounding the oil or fat, effectively creating a barrier against oxidation. Furthermore, the addition of natural or synthetic antioxidants can further protect the product from degradation.
The Role of Antioxidants in Oil Preservation
Antioxidants play a critical role in preserving oils and fats by inhibiting the oxidation process. These compounds, whether naturally occurring or synthetically produced, work by scavenging free radicals, which are highly reactive molecules that initiate and propagate the chain reactions of oxidation. This interruption of the chain reaction significantly reduces the rate of rancidity development.
Different types of antioxidants offer varying degrees of protection. For example, natural antioxidants, like vitamin E, are commonly used due to their effectiveness and generally perceived safety. Synthetic antioxidants, such as butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), also demonstrate strong antioxidant activity but have raised some safety concerns in certain contexts.
Understanding the Chemistry of Oxidation
Oxidation in oils and fats is a complex chemical process driven by the interaction of the fats' chemical structure with oxygen. Unsaturated fatty acids, which contain double bonds, are particularly susceptible to oxidation due to the reactivity of these bonds. Exposure to oxygen initiates a chain reaction that leads to the formation of off-flavors, off-odors, and even potentially harmful compounds.
The breakdown of these fats can result in the production of volatile compounds responsible for the characteristic rancid odors and tastes. This process is influenced by factors such as temperature, light, and presence of metals that act as catalysts.
Storage Conditions and Oxidation Prevention
Proper storage conditions are paramount in minimizing oxidation in oils and fats. Maintaining a cool, dark, and dry environment significantly reduces the rate of oxidation. Exposure to excessive heat accelerates the reactions, while light promotes the formation of free radicals. Using airtight containers prevents oxygen from reaching the oil or fat, thus preventing contact with the catalyst for oxidation.
Maintaining consistent temperature control, avoiding exposure to excessive light, and selecting appropriate containers are vital steps in ensuring the long-term quality and safety of the oils and fats.
Packaging Innovations and Preservation
Advancements in packaging technology offer innovative solutions for extending the shelf life of oils and fats. Modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) is a significant development that alters the gaseous environment surrounding the product, reducing the availability of oxygen. The use of specialized coatings and barriers further enhances the protection against oxidation.
The Impact of Light and Heat on Oxidation
Light and heat significantly accelerate the oxidation process in oils and fats. Sunlight, fluorescent lights, and even incandescent bulbs can trigger the formation of free radicals. Heat provides the energy necessary for the reaction to proceed at a faster rate. Therefore, storing oils and fats in opaque containers and cool places is crucial for preserving their quality and preventing undesirable changes in flavor and odor.
Minimizing exposure to both light and high temperatures helps to maintain the nutritional value and sensory characteristics of the oils and fats for longer periods, ensuring their usability and safety.