Beyond Soil: The Impact on Biodiversity and Water Resources

Ecological Interconnections
Human activities influence complex ecological networks extending far beyond surface levels. The vitality of one system directly affects others, generating ripple effects throughout global ecosystems. From plant-pollinator relationships to predator-prey balances, these connections maintain biodiversity.
Disrupting these relationships can trigger chain reactions affecting species survival and ecosystem stability. Overlooking these intricate links risks causing irreversible environmental harm.
Water's Role in Biodiversity
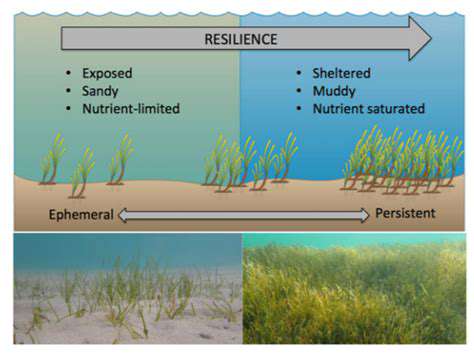
Aquatic resources sustain countless species and ecological processes, from hydration to nutrient cycling. Water quality and availability crucially impact organism survival and reproduction.
Pollution or climate-induced changes can devastate aquatic and terrestrial systems, potentially eliminating sensitive species. Protecting clean water sources remains essential for biodiversity conservation.
Atmospheric Influences
Often underestimated, atmospheric conditions profoundly affect biodiversity. Temperature, precipitation, and air quality all influence species distribution, migration patterns, and plant development.
Air Quality Concerns
Industrial emissions damage plant tissues, reduce photosynthesis, and impair animal respiration. These effects can precipitate population declines and species extinctions.
Understanding air quality's ecological impacts is vital for developing effective mitigation strategies. Combating pollution at its source proves critical for planetary health.
Solar Energy Dynamics
Sunlight drives Earth's ecosystems through photosynthesis, forming food web foundations. Variations in light availability significantly impact ecosystem productivity and energy flows.
Disruptions to these energy pathways can cascade through entire food networks, underscoring sunlight's importance in maintaining biodiversity.
The Future of Farming: Embracing Regenerative Practices

Precision Agriculture Advancements
Modern farming utilizes technological innovations to enhance efficiency while reducing environmental harm. Data-informed methods enable precise application of water, nutrients, and pest controls tailored to specific field areas. This targeted approach minimizes waste while optimizing production, advancing sustainable agriculture.
GPS, sensors, and aerial imaging provide real-time information about soil conditions and crop health. These tools empower farmers to make informed planting and irrigation decisions, improving yields while controlling costs.
Crop Improvement Through Genetics
Genetic modification offers solutions for developing resilient, high-yielding crops. Scientists are engineering plants resistant to pests, diseases, and extreme weather, benefiting farmers in challenging environments.
Enhanced nutritional content in modified crops could address global food security and public health challenges, representing a promising frontier in agricultural science.
Vertical Farming Innovations
Stacked cultivation in controlled environments presents space-efficient food production solutions. This method reduces land and water requirements, making it ideal for urban settings.
Sustainable Methodologies
Adopting earth-friendly techniques ensures long-term food security and environmental protection. Crop rotation, cover planting, and biological pest management are gaining traction among forward-thinking farmers.
These approaches preserve soil integrity, reduce chemical dependence, and support biodiversity, fostering resilient agricultural ecosystems.
Technological Integration
Digital tools revolutionize farm operations through enhanced monitoring and decision-making. Analytical software helps optimize resource allocation, production, and waste reduction.
Advanced monitoring systems track livestock health, crop progress, and soil conditions, providing actionable insights for improved management. This technological transformation drives efficiency and profitability.
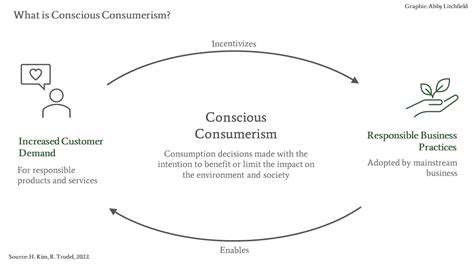
Evolving Consumer Expectations
Growing demand for sustainable, ethically produced food is reshaping agriculture. Increasing environmental awareness influences purchasing decisions, creating opportunities for eco-conscious producers.
Future agricultural success depends on meeting these changing consumer preferences while ensuring sector sustainability, balancing economic and environmental considerations.