Fermentation: Harnessing Beneficial Microbes
Understanding the Role of Microbes
Fermentation uses beneficial microorganisms, mainly bacteria and yeast, to transform food. These tiny organisms change food through their natural processes, preserving it while often improving flavor and nutrition. Understanding how these microbes work is essential for successful fermentation. Their metabolic activities and interactions with food determine the final product's qualities.
Different microbes have specific roles in fermentation, depending on the food, desired outcome, and environment. Choosing the right microbial culture is crucial for both food safety and achieving the intended results.
The Chemistry Behind Fermentation
Fermentation involves complex chemical reactions powered by microbial enzymes. These reactions break down food components like sugars and proteins into simpler compounds. This process creates energy and produces the distinctive flavors, textures, and smells of fermented foods. The specific changes depend on the fermentation type and microbes involved.
Types of Fermentation Processes
Fermentation includes many methods with unique characteristics. Lactic acid fermentation makes foods like sauerkraut and yogurt. Alcoholic fermentation produces beer and wine. Acetic acid fermentation creates vinegar. Knowing these differences helps select the right method for each food.
Each fermentation type creates different byproducts that affect the food's taste, texture, and nutrition. For example, lactic acid fermentation's tangy flavor comes from the acid that also preserves the food by creating an inhospitable environment for harmful bacteria.
Factors Influencing Fermentation Success
Several factors affect fermentation outcomes. Temperature, acidity, and available nutrients all influence microbial activity. Maintaining ideal conditions ensures good results and food safety. Starting with high-quality ingredients also significantly impacts the final product.
Food Preservation Through Fermentation
Fermentation is an ancient preservation method that works by creating conditions unfavorable to spoilage organisms. This extends food's shelf life while often improving its taste and nutritional value. In areas without reliable refrigeration, fermentation remains a vital food preservation technique.
Nutritional Benefits of Fermented Foods
Fermented foods often offer more nutrition than their unfermented versions. The process can make nutrients easier to digest and absorb. Many fermented foods contain probiotics - live microbes that benefit digestion and immunity. Growing awareness of these health benefits has increased fermented foods' popularity in healthy diets.
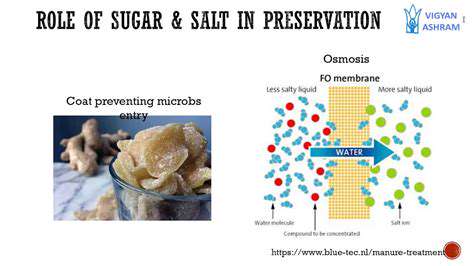
Other Natural Preservation Methods: Salt Curing and Sugaring
Protecting Habitats
Preserving natural habitats is essential for maintaining biodiversity. Key areas like forests, wetlands, and coasts need special protection. Conservation efforts include creating protected zones like national parks to reduce human impact and support native species. These areas provide safe spaces for plants and animals to live and reproduce.
Restoring damaged ecosystems is equally important. Projects might involve replanting native species, removing invasive plants, or fixing water systems. These actions create stronger ecosystems that can better handle environmental stresses and support more life.
Sustainable Resource Management
Responsible resource use helps minimize environmental damage. Sustainable forestry and fishing practices ensure these resources remain available for the future. This includes selective logging, replanting trees, and setting fishing limits to prevent overharvesting.
Controlling Invasive Species
Non-native species can disrupt ecosystems by competing with local plants and animals. Early detection and targeted removal are crucial for controlling invasive species. Public education about how to prevent their spread is also important.
Control methods range from physical removal to using natural predators. Careful planning prevents unintended ecological impacts. Keeping ecosystems balanced should be the priority in invasive species management.
Promoting Sustainable Agriculture
Eco-friendly farming helps protect the environment while producing food. Techniques like crop rotation and natural pest control reduce agriculture's environmental impact. These methods improve soil health, save water, and cut chemical use. Sustainable farms also provide habitats for wildlife.
Reducing Pollution
Pollution from industry, farming, and waste harms natural environments. Tighter pollution controls and cleaner technologies help protect air and water quality. Reducing pollution benefits both nature and human health.
Education and Awareness
Teaching people about environmental protection is vital for conservation. Understanding how ecosystems work and how humans affect them encourages better choices. Environmental education programs and community projects help build a sustainable future. Involving young people in conservation helps create lifelong environmental stewards.