The Rise of Agribusiness Monopolies and Their Impact
The Consolidation of Power
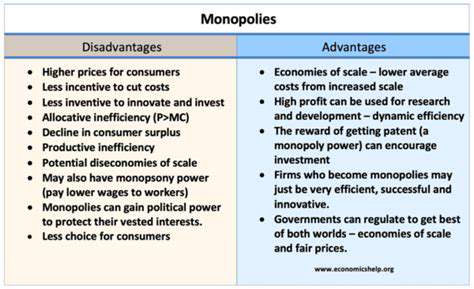
The agricultural sector has experienced a significant shift towards consolidation, with larger corporations acquiring smaller farms and agricultural businesses. This trend has led to a concentration of market power in the hands of a few major players, often referred to as agribusiness monopolies. This consolidation has implications for both farmers and consumers. Farmers may find themselves at the mercy of these powerful entities, potentially facing unfavorable pricing and limited market access. Consumers may also experience higher prices and reduced product variety.
The Impact on Farmers
Farmers, especially smaller family farms, often find themselves at a disadvantage in the face of agribusiness monopolies. These large corporations often have access to significant resources, including advanced technology, extensive land holdings, and sophisticated supply chains. This puts smaller farms at a competitive disadvantage, and can make it difficult for them to compete and thrive in the market. The ability of independent farmers to maintain their businesses and livelihoods is threatened.
Moreover, the terms and conditions imposed by these companies can be restrictive, potentially limiting the farmers' autonomy and control over their operations. This can lead to reduced profitability and diminished quality of life for farmers.
Vertical Integration Strategies
Agribusiness monopolies often employ vertical integration strategies, which involve controlling multiple stages of the food production process, from seed to sale. This allows them to exert greater control over the supply chain, maximizing profits and minimizing costs. Vertical integration can significantly impact the market dynamics, creating challenges for competitors. These companies often own or control seed production, processing facilities, distribution networks, and retail outlets, giving them a significant advantage over smaller players. This control over the entire supply chain allows them to dictate prices and terms, further consolidating their market power.
Market Dominance and Pricing Power
The dominance of agribusiness monopolies in specific agricultural sectors can lead to significant pricing power. This means that these companies have the ability to influence the prices of agricultural products, potentially impacting both farmers and consumers. High prices for agricultural products can negatively affect consumers, limiting affordability and potentially creating economic hardship. Their immense market share allows them to dictate terms and conditions, impacting the overall market dynamics and potentially creating a less competitive environment.
Globalization and Trade Agreements
Globalization and international trade agreements play a significant role in the rise of agribusiness monopolies. Free trade agreements often facilitate the expansion of multinational corporations into new markets, giving them access to broader resources and increased market share. This expansion can contribute to the consolidation of the industry, potentially leading to the dominance of a few powerful players. Furthermore, international trade policies can influence the pricing of agricultural products, impacting the profitability of both large and small farms.
Regulatory and Policy Responses
Addressing the rise of agribusiness monopolies requires careful consideration of regulatory and policy responses. Governments need to implement policies that promote competition and prevent excessive market concentration. Stronger antitrust regulations are essential to prevent the formation of monopolies or the abuse of market dominance. These measures can help ensure a more level playing field for smaller farms and promote fair competition in the agricultural sector. Policies focused on supporting small farms and promoting sustainable agricultural practices can also help mitigate the negative impacts of agribusiness consolidation.












