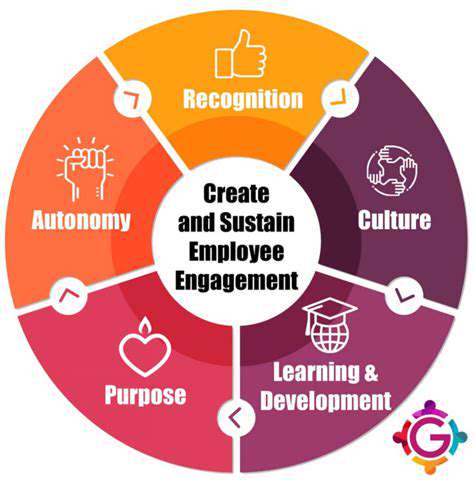
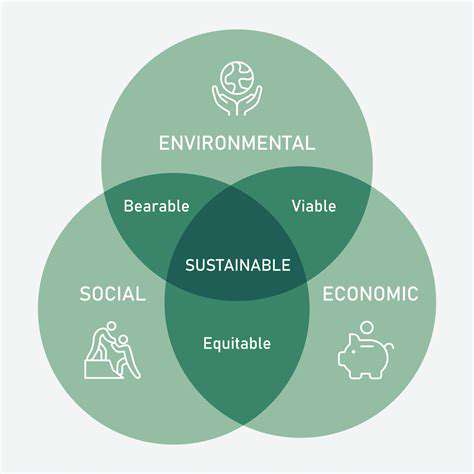
Highlighting the Environmental and Social Impacts of Food
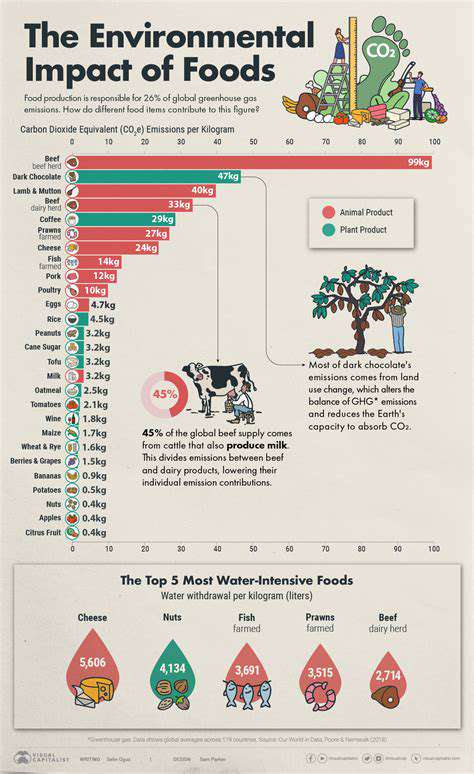
Environmental Impact of Plastics
Our planet faces an unprecedented challenge with plastic pollution, which disrupts ecosystems across all levels. From microscopic organisms to majestic marine creatures, no lifeform remains untouched by this synthetic invasion. Each year, millions of tons of plastic waste enter our environment, overwhelming disposal systems and accumulating in our waterways and landscapes.
The consequences manifest tragically in marine environments where creatures frequently mistake plastic debris for nourishment, leading to fatal consequences. Even more insidiously, these plastics break down into microplastics that infiltrate food chains, ultimately finding their way onto our dinner plates through contaminated seafood.
Sustainable Alternatives to Plastic
As awareness grows about plastic's detrimental effects, innovative solutions are emerging. While biodegradable options show potential, they often come with their own limitations regarding decomposition rates and chemical byproducts. Creating truly sustainable replacements requires comprehensive strategies that address both material development and waste processing infrastructure.
Materials derived from renewable sources like bamboo and plant starches, combined with advanced recycling methods, represent promising paths forward. Though these alternatives present exciting possibilities, they require further refinement to achieve widespread practical application and environmental benefit.
Plastic Recycling and Waste Management
Addressing plastic pollution demands substantial improvements in recycling and waste handling systems. Current facilities often struggle with the variety of plastic types and contamination issues in waste streams. Investments in advanced sorting technologies and specialized processing plants could dramatically enhance recycling effectiveness.
Equally important are initiatives that encourage consumers to reduce plastic use through education and incentives for reusable alternatives. These behavioral changes, supported by strong policy frameworks, form essential components of long-term solutions.
The Role of Policy and Legislation
Governments wield significant influence in combating plastic pollution through thoughtful regulation. Comprehensive policies governing plastic production, use, and disposal can effectively steer both corporate and consumer behavior toward sustainability. Extended producer responsibility programs create powerful incentives for manufacturers to prioritize environmentally friendly design throughout product lifecycles.
Policy tools like single-use plastic taxes and subsidies for sustainable alternatives encourage market shifts toward circular economic models where materials remain in productive use rather than becoming waste.
Addressing the Global Scope of Plastic Pollution
Plastic pollution knows no borders, demanding coordinated international action. Shared knowledge and standardized approaches to waste management enable more effective solutions across regions. Collaborative efforts connecting researchers, policymakers, and industry leaders accelerate progress in developing sustainable materials and improving recycling technologies.
Multinational agreements targeting ocean plastics demonstrate the potential of collective action to address this pressing environmental challenge on the global stage.
Promoting Eco-Friendly Packaging and Reducing Waste
Understanding the Consumer Shift Towards Eco-Friendly Packaging
Modern shoppers increasingly factor packaging sustainability into purchasing decisions, reflecting deeper environmental awareness. This paradigm shift transcends mere convenience as consumers actively seek products aligned with their ecological values. Forward-thinking companies recognize this trend as both a responsibility and opportunity to strengthen brand loyalty through demonstrated environmental stewardship.
The Role of Eco-Friendly Packaging in Sustainable Food Marketing
Environmentally conscious packaging serves as a powerful brand differentiator in competitive markets. By reducing waste and utilizing sustainable materials, companies can establish themselves as sustainability leaders while appealing to growing consumer demand for responsible practices.
Innovative Materials for Eco-Friendly Packaging
The packaging industry continues evolving with groundbreaking materials including biodegradable polymers, plant-derived alternatives, and advanced recycled content. These developments help reduce dependence on finite resources while maintaining product protection standards.
Minimizing Waste Through Packaging Design
Strategic packaging design significantly reduces material usage without compromising functionality. Optimized dimensions, weight reduction, and material selection all contribute to waste reduction while ensuring product integrity throughout distribution channels.
The Economic Benefits of Eco-Friendly Packaging
Beyond environmental advantages, sustainable packaging delivers measurable business benefits including operational efficiencies, enhanced brand perception, and access to environmentally conscious market segments.
Emphasizing Local and Seasonal Produce
Understanding the Value of Local Produce
Local food systems create virtuous cycles benefiting communities and environments alike. Reduced transportation distances lower carbon footprints while keeping food dollars circulating locally to support regional economies.
The Environmental Benefits of Seasonal Eating
Seasonal consumption patterns naturally align with ecological rhythms, minimizing energy-intensive production methods while delivering peak flavor and nutrition.
Health Benefits of Fresh, Local Produce
Locally sourced items harvested at optimal ripeness offer superior nutritional profiles compared to produce that undergoes extended storage and transport.
Showcasing Sustainable Farming Practices
Improving Soil Health
Regenerative agricultural methods prioritize soil vitality through techniques like cover cropping and organic amendments. Healthy soils demonstrate remarkable water retention capabilities while supporting diverse microbial communities essential for plant health.
Diversifying Crop Production
Polyculture systems enhance ecosystem resilience by reducing pest pressures and improving nutrient cycling compared to monoculture approaches.
Implementing Water Conservation Techniques
Precision irrigation systems and moisture-retentive soil management practices help conserve water resources while maintaining crop productivity.