Processed meats, such as bacon, sausage, and hot dogs, are incredibly popular, but their seemingly harmless nature often masks significant health implications. These products are often loaded with preservatives and nitrates, which have been linked to increased risks of various cancers, heart disease, and other chronic illnesses. Understanding the long-term effects of regularly consuming processed meats is crucial for making informed dietary choices.
Beyond the potential health risks, the environmental impact of processed meat production should also be considered. The intensive farming practices used to raise livestock for these products contribute to deforestation, greenhouse gas emissions, and water pollution. These factors highlight a broader systemic issue of unsustainable food production.
Sugary Drinks: Empty Calories and Empty Promises
Sugary drinks, including sodas, juices, and sweetened teas, are a significant contributor to the rising rates of obesity and related health problems. These beverages are often devoid of essential nutrients, providing only empty calories that can lead to weight gain and metabolic issues. The constant consumption of these drinks can also disrupt blood sugar regulation and increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.
The widespread availability and often perceived convenience of sugary drinks make them a pervasive part of modern diets. However, understanding their negative impact on health and well-being is essential for making healthier choices.
Refined Grains: A Closer Look at Empty Promises
Refined grains, such as white bread, white rice, and pasta, are often used in countless dishes, yet their nutritional value is significantly lower compared to their whole-grain counterparts. The refining process strips away the bran and germ, removing essential nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and minerals. This lack of essential nutrients often leads to a rapid rise in blood sugar levels, which can contribute to various health issues.
While refined grains might seem like an easy choice for quick meals, they frequently lack the sustained energy and essential nutrients necessary for optimal health and well-being. Focusing on whole grains offers a more nutritious and balanced dietary approach.
Fast Food: Convenience at a Cost
Fast food restaurants are ubiquitous, offering quick and convenient meals. However, these meals often contain high levels of saturated and trans fats, sodium, and added sugars. This combination of ingredients can contribute to weight gain, high blood pressure, and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The reliance on fast food for regular meals can severely impact long-term health.
Beyond the individual health implications, the environmental impact of fast food production should not be overlooked. The production and transportation of ingredients and the waste generated by the industry contribute to environmental degradation. Adopting more mindful dietary choices can contribute to a healthier planet.
Hidden Fats and Trans Fats: Sneaking Into Your Diet
Many processed foods contain hidden fats, often in the form of partially hydrogenated oils. These oils are a major source of trans fats, which have been linked to various health problems. Trans fats can raise LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and lower HDL (good) cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease. Understanding the hidden sources of trans fats in our diet is crucial for preventing these negative health outcomes.
The use of trans fats has been restricted in many countries due to their negative health effects. However, it is still important to be aware of the possibility of hidden trans fats in processed foods and choose healthier alternatives whenever possible. Careful food labeling and awareness of ingredients can help consumers make informed choices.
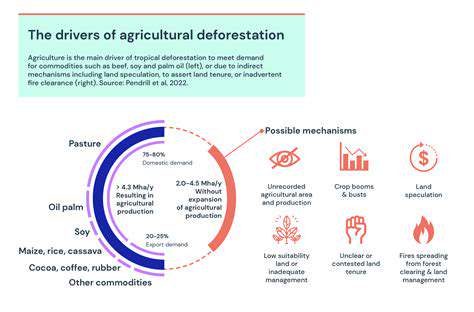
Meat Consumption and its Environmental Impact

Meat Consumption's Impact on the Environment
The global demand for meat, particularly red meat like beef and lamb, is placing a significant strain on the environment. Raising livestock for meat production requires vast amounts of land, leading to deforestation and habitat loss for countless species. The conversion of natural ecosystems into pastureland and feed crops contributes to biodiversity decline and disrupts delicate ecological balances.
Furthermore, the agricultural practices associated with meat production often involve intensive use of fertilizers and pesticides. These chemicals can contaminate water sources, harming aquatic life and potentially impacting human health. The runoff from these agricultural activities also contributes to water pollution, creating dead zones in some bodies of water.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Meat Production
Livestock farming is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, largely from methane produced by animals' digestive systems. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, trapping significantly more heat in the atmosphere compared to carbon dioxide over a 20-year timeframe. This contributes to climate change, a phenomenon with far-reaching consequences for global ecosystems and human societies.
Beyond methane, the production of animal feed, transportation of livestock and meat products, and manure management all release significant amounts of greenhouse gases. These emissions compound the overall impact on the environment, accelerating global warming and its associated effects, such as rising sea levels and extreme weather events.
Sustainable Alternatives to Conventional Meat Consumption
Recognizing the environmental consequences of excessive meat consumption, there's a growing movement towards more sustainable alternatives. Plant-based meat substitutes offer a compelling way to reduce our environmental footprint. These alternatives often require significantly less land and resources to produce, reducing the strain on natural ecosystems.
The Role of Individual Choices and Policy Changes
Individual choices play a crucial role in mitigating the environmental impact of meat consumption. Consumers can make conscious decisions to reduce their meat intake, opting for plant-based protein sources more frequently. Supporting sustainable farming practices and choosing locally sourced, high-quality meat can also contribute to a more environmentally responsible food system.
Policy changes at the governmental level can further encourage sustainable practices. Incentivizing the adoption of sustainable farming methods and providing support for research into alternative protein sources can create a more environmentally friendly food system. These policies can stimulate innovation and drive change in the long term.
Quantum computing represents a paradigm shift in information processing, leveraging the bizarre and counterintuitive properties of quantum mechanics to perform calculations that are impossible for even the most powerful classical computers. This novel approach promises to revolutionize fields ranging from drug discovery to materials science, potentially unlocking solutions to some of humanity's most pressing challenges. Quantum computers utilize qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously, unlike classical bits that are either 0 or 1. This superposition allows for exponentially faster computations in certain scenarios.