Defining the Concept
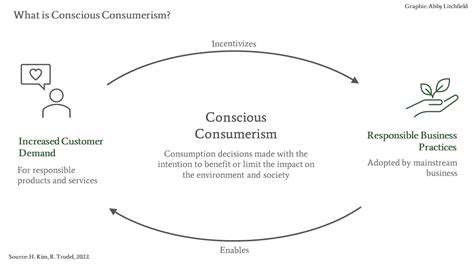
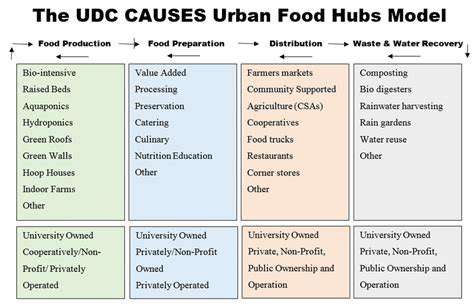
Urban food hubs represent dynamic, multifaceted spaces that act as critical connectors within urban food networks. These hubs integrate diverse elements like community gardens, farmers' markets, processing centers, and retail operations. Far beyond mere physical locations, they serve as vital nexus points linking producers, consumers, and neighborhoods. Their role in combating food insecurity and advancing sustainable urban food systems cannot be overstated.
What truly sets urban food hubs apart is their dual focus on infrastructure and socioeconomic development. By creating pathways for local farmers, small business owners, and residents to thrive, these spaces simultaneously enhance community vitality. This comprehensive approach clearly differentiates them from standalone farmers' markets or gardening initiatives.
Key Components of a Hub
Effective urban food hubs share several fundamental characteristics. They provide essential shared resources - think cold storage units and food processing equipment - alongside educational programming and community gatherings. The lifeblood of these hubs flows from active community participation and cooperative spirit. This collective engagement fosters deep-rooted investment in the hub's success.
Equally important are financial access points, entrepreneurial training, and mentorship initiatives. These resources empower local food producers and business owners to refine their operations, expand their customer base, and achieve greater market stability. Such support systems prove indispensable for maintaining hub viability over time.
Local Food System Integration
Urban food hubs function as linchpins within broader regional food networks. They bridge the gap between growers and eaters, shortening supply routes while decreasing food transportation's environmental toll. This integration frequently involves strategic partnerships with nearby farms, food artisans, and culinary establishments. By bolstering local agriculture and food enterprises, these hubs reinforce regional economic stability and ecological sustainability.
These close-knit connections guarantee fresher, more flavorful produce reaches consumers. A well-developed network of local suppliers within the hub framework ensures diverse, appealing food options for community members. This hyperlocal sourcing model also dramatically cuts the food system's carbon emissions.
Community Impact and Sustainability
The influence of urban food hubs extends well beyond economics and ecology to community wellness. They serve as platforms for skill-building and nutritional education, cultivating neighborhood pride and ownership. These hubs frequently tackle food access challenges, ensuring residents can obtain affordable, nutritious sustenance.
Sustainability principles guide every aspect of urban food hub operations. They work to shrink environmental impacts while amplifying social and economic benefits through sustainable growing methods, waste reduction strategies, and energy-efficient designs. This unwavering commitment to sustainability forms the foundation for these spaces' enduring community value.
The Economic Benefits of Local Food Systems

Supporting Local Farmers and Businesses
Local food system investments generate economic momentum within communities. When consumers choose locally grown products, they directly fuel regional businesses, sparking job creation and economic circulation. This patronage strengthens agricultural foundations, encouraging more resilient and sustainable farming approaches. For small-scale producers, these direct sales channels provide essential income streams and operational security, enabling them to continue delivering premium local produce.
Additionally, localized food economies birth new entrepreneurial ventures - from specialty farmers' markets to restaurants highlighting regional ingredients and community-supported agriculture programs.
Reduced Transportation Costs and Emissions
Prioritizing local food yields substantial transportation efficiencies. Long-distance food shipping demands excessive energy, driving up fuel consumption and carbon outputs. Choosing local suppliers dramatically cuts food transportation's environmental burden, decreasing fossil fuel dependence and benefiting planetary health. This shift toward regional food networks makes tangible contributions to climate change mitigation efforts.
Shorter transit times also mean consumers enjoy fresher, higher-quality products that haven't endured lengthy shipping and handling processes.
Increased Food Security and Supply Chain Resilience
Regional food networks enhance food security through diversified, robust supply channels. This diversification buffers communities against global supply disruptions, creating more reliable food access points. Local producers remain less vulnerable to international market volatility and large-scale disasters that can destabilize food availability and pricing. The resulting stability significantly improves household food security.
This localized production and distribution model establishes more dependable food supplies, minimizing shortage risks and price fluctuations caused by external factors.
Enhanced Food Quality and Taste
Locally sourced foods typically offer superior quality and flavor profiles due to minimal transit times and optimal harvest timing. Peak freshness becomes the standard, with local crops picked at perfect ripeness for maximum flavor and nutritional content. Consumers experience noticeably better taste and texture in locally grown products compared to their long-distance counterparts.
The sensory qualities of freshly harvested local produce create eating experiences that mass-distributed foods simply cannot match.
Promoting Health and Well-being
Diets rich in fresh, locally grown foods correlate with numerous health advantages. Consuming regional produce delivers higher concentrations of nutrients and antioxidants, supporting overall wellness. Access to fresh, minimally processed foods helps reduce chronic disease rates while improving community health metrics. This direct connection to food sources also cultivates greater appreciation for what we consume.
Supporting local agriculture fosters healthier lifestyle choices while promoting sustainable consumption patterns within communities.
Strengthening Community Bonds
Local food initiatives powerfully reinforce social connections. Farmers' markets and community gardens become vibrant gathering spaces where knowledge sharing and relationship building flourish. These shared experiences weave stronger social fabrics and nurture genuine community belonging. Beyond economic benefits, local food systems enhance overall quality of life for all participants.
Investing in local food enterprises yields dividends that extend far beyond financial returns to include social cohesion and community pride.
The Future of Food: Scaling Up Sustainable Solutions

Sustainable Agriculture Practices for Increased Yields
Contemporary agriculture must balance rising global food demands with environmental stewardship. Sustainable farming methods offer solutions, incorporating precision agriculture technologies that maximize resource efficiency while minimizing waste. These approaches can substantially reduce food production's ecological impact while ensuring agricultural sustainability. Techniques like rotational planting enhance soil vitality, while integrated pest management decreases chemical pesticide reliance.
Water conservation represents another critical component. Advanced irrigation systems and drought-hardy crop varieties help reduce agricultural water consumption. As water scarcity intensifies globally, these practices become increasingly vital for maintaining food production stability.
Vertical Farming and Controlled Environments
Vertical farming presents an innovative response to conventional agriculture's limitations. By cultivating crops in stacked, climate-controlled environments, this method conserves land while potentially boosting yields through optimized growing conditions. The urban placement of vertical farms offers additional advantages by slashing food transportation distances and related emissions.
This urban proximity proves particularly valuable for addressing food access disparities in cities while strengthening local food security networks.
Precision Agriculture and Data-Driven Solutions
Modern precision agriculture harnesses technology to improve farming efficiency. Sensor networks, aerial drones, and analytical tools enable real-time monitoring of crop health, soil conditions, and resource utilization. This data-centric methodology allows precise interventions that maximize productivity while minimizing environmental strain.
Satellite imaging and GPS technologies further enhance monitoring capabilities, enabling more efficient application of water, fertilizers, and pest controls to reduce agriculture's ecological footprint.
Gene Editing and Genetic Modification
Breakthroughs in gene editing, particularly CRISPR technology, are transforming crop development. These tools enable precise genetic modifications that enhance desirable traits like pest resistance, drought tolerance, and nutritional density. Such targeted improvements can produce hardier crops capable of thriving in challenging environmental conditions.
Alternative Protein Sources: Beyond Traditional Meats
Growing global meat demand strains conventional livestock systems. Plant-based alternatives and lab-cultured meats offer promising solutions to reduce the environmental impacts of animal agriculture, including greenhouse gas emissions and land use pressures. The expanding plant-based protein market represents a significant step toward more sustainable food systems.
Food Waste Reduction and Efficient Distribution
Food waste remains a critical challenge across global supply chains. Implementing comprehensive waste reduction strategies - from improved storage methods to consumer education - can dramatically decrease food loss. Minimizing waste not only conserves resources but also reduces unnecessary environmental burdens. Optimized distribution networks help ensure more food reaches consumers while reducing spoilage rates.