Addressing Gut Imbalance: Dietary Strategies for a Healthier Gut

Understanding the Importance of Gut Health
A healthy gut microbiome is crucial for overall well-being, impacting everything from digestion and nutrient absorption to immune function and mental health. Maintaining a balanced gut ecosystem is essential for preventing various health issues. Many factors contribute to gut imbalances, including poor diet, stress, and certain medications, and these imbalances can lead to a cascade of negative effects throughout the body. Understanding the role of diet in maintaining a healthy gut is therefore paramount.
The gut microbiome, a complex community of microorganisms residing in the digestive tract, plays a vital role in numerous bodily functions. A balanced gut microbiome is characterized by a diverse range of beneficial bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms that work in harmony to support optimal health. Disruptions to this balance can lead to digestive issues, immune deficiencies, and even mental health problems.
Dietary Strategies for Restoring Gut Balance
Prioritizing a diverse range of nutrient-rich foods is key to fostering a thriving gut microbiome. Incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes provides the essential fiber and prebiotics needed to feed beneficial gut bacteria. This dietary approach allows for a more comprehensive approach to gut health.
Reducing processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive intake of saturated fats can significantly improve gut health. These foods often contain ingredients that can negatively impact the gut microbiome and contribute to inflammation. Minimizing these detrimental components is crucial for restoring a healthy gut ecosystem. Choosing whole, unprocessed foods will provide a balanced and beneficial approach to your diet.
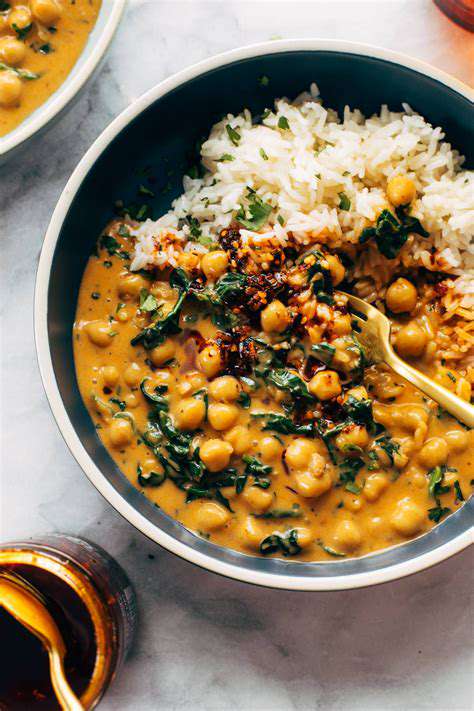
Fermented foods, rich in beneficial bacteria, can also be beneficial for promoting gut health. These foods provide a source of probiotics, which are live microorganisms that can help repopulate the gut with beneficial bacteria. Including fermented foods in your diet can be a powerful strategy for improving gut health. Examples include yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut.
The Role of Diet in Maintaining a Healthy Gut Microbiome
A diet rich in fiber is crucial for supporting a healthy gut microbiome. Fiber acts as a prebiotic, feeding the beneficial bacteria in the gut and promoting their growth. Consuming adequate amounts of fiber ensures that the good bacteria are well-nourished. This can help maintain a balanced gut ecosystem.
Variety in your diet is important for a healthy gut. A balanced diet including various fruits, vegetables, and whole grains ensures that the microbiome receives a wide range of nutrients, promoting optimal function. A diverse diet is vital for supporting the health and diversity of the gut microbiome.
The Power of a Balanced Plate: Creating a Gut-Friendly Diet Plan

Fueling Your Body for Optimal Health
A balanced plate, a cornerstone of healthy eating, provides your body with the essential nutrients it needs to thrive. This balanced intake of macronutrients – protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats – is crucial for energy production, muscle repair, and overall well-being. Understanding the proportions of each food group is key to harnessing the power of a balanced plate and achieving your health goals.
By incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains into your meals, you're not only fueling your body with the vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants it needs but also promoting satiety and preventing overeating. A balanced diet supports a healthy weight, strong immune function, and improved cognitive function.
Prioritizing Protein for Muscle Growth and Repair
Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, including muscles. Including lean protein sources in your diet is vital for individuals engaging in regular physical activity, as it helps support muscle growth and repair. Excellent sources of protein include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, beans, lentils, and tofu.
Consuming adequate protein is also beneficial for maintaining a healthy weight. Protein promotes satiety, which can help regulate appetite and prevent overeating throughout the day.
Harnessing the Power of Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which are crucial for a variety of bodily functions. They contribute significantly to a healthy immune system and help protect against chronic diseases. Aim for a colorful array of fruits and vegetables to maximize your intake of diverse nutrients.
The Importance of Whole Grains for Sustained Energy
Whole grains are an excellent source of complex carbohydrates, providing sustained energy throughout the day. They are also rich in fiber, which aids in digestion and helps regulate blood sugar levels. Choosing whole grains over refined grains is a significant step toward a healthier diet.
Incorporating whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole-wheat bread into your meals can contribute to a more balanced and satisfying eating experience. This sustained energy release promotes better focus and concentration, especially beneficial during periods of high activity.
Healthy Fats for Brain Function and Overall Health
Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, are essential for brain function, hormone production, and overall health. These fats are critical for cell growth and repair, and also play a vital role in absorbing fat-soluble vitamins. Including these foods in your diet can help improve cardiovascular health.
A balanced intake of healthy fats is also linked to improved cognitive function and reduced inflammation in the body. They are integral to various bodily processes, supporting overall well-being and contributing to a healthier lifestyle.