Environmental Benefits and Sustainability
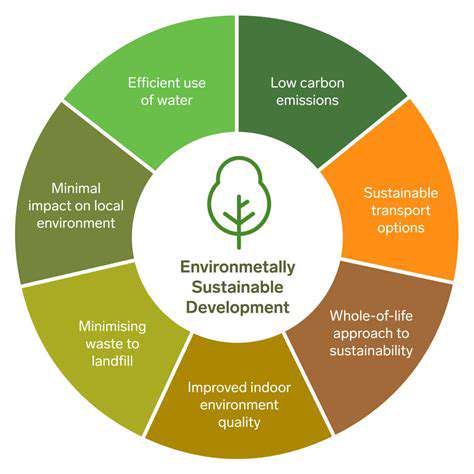
Environmental Conservation Efforts
Protecting our environment is crucial for the well-being of future generations. Implementing sustainable practices is not just a trend, but a fundamental responsibility we all share. Conserving natural resources, such as forests and water, is essential to maintain ecological balance and prevent biodiversity loss. These efforts often involve reducing pollution, promoting renewable energy sources, and implementing responsible land management strategies.
Protecting endangered species and their habitats is another vital aspect of environmental conservation. Many species face threats from habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change. Dedicated conservation initiatives aim to safeguard these fragile ecosystems and the creatures that call them home. These efforts often involve establishing protected areas, implementing conservation breeding programs, and tackling the root causes of species decline.
Sustainable Resource Management
Sustainable resource management focuses on utilizing natural resources in a way that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This approach emphasizes responsible harvesting, minimizing waste, and promoting the use of renewable resources.
Careful planning and monitoring are key components of sustainable resource management. This ensures that the exploitation of resources is balanced with the preservation of ecological integrity. For example, sustainable forestry practices involve selective logging and reforestation efforts.
Pollution Reduction and Control
Reducing and controlling pollution is a critical aspect of environmental sustainability. Air pollution, water pollution, and soil contamination have severe consequences for human health and the environment. Implementing stricter emission standards and promoting cleaner technologies are vital steps in reducing pollution levels.
Promoting the use of public transportation, encouraging the development of electric vehicles, and supporting sustainable agricultural practices are all important strategies for reducing pollution. By collectively working towards cleaner solutions, we can mitigate the impact of pollution on our planet.
Renewable Energy Sources
Transitioning to renewable energy sources is crucial for mitigating climate change and reducing our dependence on fossil fuels. Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydro power, are naturally replenished and have a significantly lower environmental impact compared to traditional energy sources.
Investing in renewable energy infrastructure and developing innovative technologies for harnessing renewable energy are essential for a sustainable future. This shift towards sustainable energy sources can help create a more resilient and cleaner energy system.
Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation
Addressing climate change is one of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time. The effects of climate change, such as rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and disruptions to ecosystems, are already being felt worldwide. Efforts to mitigate climate change must focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable practices.
Adapting to the unavoidable impacts of climate change is also essential. This includes developing strategies for managing water resources, protecting coastal communities, and strengthening infrastructure to withstand extreme weather events. Climate change adaptation strategies are vital for building resilience and ensuring the well-being of communities in the face of these challenges.
Technological Advancements Driving Vertical Farming Innovation
Vertical Farming's Growing Reliance on AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming vertical farming operations, enabling precision control and optimization across the entire process. AI-powered systems analyze environmental data, such as light intensity, temperature, and humidity, in real-time, adjusting growing conditions to maximize crop yield and quality. This data-driven approach ensures optimal resource utilization, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency. Furthermore, AI algorithms can identify potential issues like disease outbreaks or nutrient deficiencies early on, allowing for proactive intervention and preventing significant crop losses.
The Power of Automation in Vertical Farms
Automation is playing a crucial role in streamlining vertical farming operations, from planting and harvesting to pest control and environmental monitoring. Automated systems can handle tasks like transplanting seedlings, watering plants, and even harvesting produce with remarkable accuracy and speed. This not only reduces labor costs but also minimizes human error, ensuring consistent quality and high production output. Furthermore, automated systems can operate 24/7, optimizing production and maximizing yield in a cost-effective manner.
Advanced Hydroponics and Aeroponics Systems
Advancements in hydroponics and aeroponics systems are revolutionizing vertical farming techniques. These soilless systems enable vertical farms to optimize water usage and nutrient delivery to plants. Hydroponics involves growing plants in nutrient-rich water solutions, while aeroponics suspends plants in the air and mists them with nutrient solutions. These systems offer significant benefits, including reduced water consumption, enhanced nutrient uptake, and increased crop yields per square foot, making them ideal for optimizing space utilization in vertical farms.
Innovative Lighting Technologies for Optimal Growth
Vertical farms are increasingly adopting advanced lighting technologies to mimic natural sunlight and optimize plant growth. LED lighting systems, in particular, are gaining popularity due to their energy efficiency, customizable spectrum, and ability to precisely control light intensity and duration. This precise control allows growers to tailor light conditions to the specific needs of various crops, promoting faster growth and higher yields. Furthermore, LED lighting systems significantly reduce energy consumption compared to traditional high-intensity discharge (HID) lighting.
Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering in Vertical Farming
Biotechnology and genetic engineering are emerging as critical tools for developing more resilient and productive crops suitable for vertical farming environments. Scientists are exploring ways to enhance crop yields, improve nutritional content, and increase disease resistance. This research could lead to the development of crops that thrive in the controlled environments of vertical farms, further increasing efficiency and sustainability. These advancements in biotechnology hold the promise of optimizing crop characteristics and potentially revolutionizing vertical farming techniques.
The Future of Food: Vertical Farming's Potential and Challenges
Vertical Farming: A Sustainable Solution?
Vertical farming, the practice of cultivating crops in vertically stacked layers, presents a compelling solution to the growing global demand for food while mitigating the environmental impact of traditional agriculture. By maximizing space utilization and minimizing land usage, vertical farms can potentially produce significantly higher yields compared to conventional farming methods. This innovative approach leverages controlled environments to optimize growing conditions, reducing reliance on unpredictable weather patterns and maximizing resource efficiency in terms of water and fertilizers.
The potential for year-round production, coupled with the ability to cultivate crops in urban areas, makes vertical farming a promising strategy for addressing food security and reducing transportation costs. This localized production can contribute to a more sustainable food system, minimizing the environmental footprint associated with long-distance food transportation and reducing the carbon emissions associated with global supply chains.
Overcoming the Hurdles of Vertical Farming
Despite its potential, vertical farming faces several significant challenges. One major hurdle is the substantial upfront investment required for constructing and equipping vertical farms. The sophisticated infrastructure, including climate control systems, lighting, and hydroponic or aeroponic systems, demands considerable capital outlay. Moreover, maintaining the optimal environmental conditions within these controlled environments can be energy-intensive, potentially offsetting some of the environmental benefits if not powered by renewable sources.
Furthermore, the development and scaling of vertical farming technologies remain in their nascent stages. Standardization of growing techniques, the optimization of crop yields, and the development of cost-effective solutions for various crops are crucial areas for ongoing research and development. Ensuring consistent quality and yield across different vertical farm operations is also a challenge that needs to be addressed for wider market acceptance.
The Future of Food Production: Exploring the Possibilities
Vertical farming offers the tantalizing prospect of revolutionizing food production. Its potential to address food security challenges, enhance resource efficiency, and contribute to a more sustainable food system is undeniable. The ongoing evolution of vertical farming technology, coupled with advancements in automation and robotics, promises to further refine the process and overcome the current challenges.
Further research and development into optimizing crop yields, reducing energy consumption, and creating more affordable solutions are crucial steps towards widespread adoption. The continued exploration of innovative techniques, including the use of vertical farms for specific niche crops and the development of vertical farm models tailored to diverse climates, will be critical in unlocking the full potential of this transformative agricultural approach.
The integration of vertical farming with other sustainable practices, such as urban gardening and community-supported agriculture, can potentially create a more resilient and equitable food system, empowering communities and reducing reliance on centralized food distribution networks.
The potential of vertical farming to reshape our approach to food production is immense, but its widespread adoption hinges on overcoming the existing challenges and continuing to refine the technology for optimal results.
Ultimately, the future of food may well be intertwined with the success and refinement of vertical farming.











