Nutrient Timing and Anti-Aging Impact
Nutrient Timing for Cellular Repair
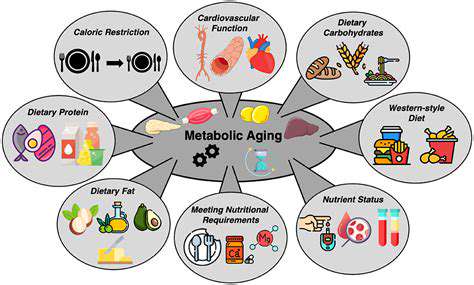
Understanding nutrient timing, particularly in relation to cellular repair, is crucial for anti-aging strategies. Timing the intake of specific nutrients around key physiological processes, like sleep and exercise, can optimize their absorption and utilization. This approach is more than just eating a healthy diet; it's about strategically consuming nutrients to support the body's natural repair mechanisms, which are critical for combating age-related decline.
Cellular repair is a complex process that involves the constant turnover of cells. Nutrients play a vital role in this process, providing the building blocks and energy needed for cell regeneration and maintenance. By focusing on nutrient timing, we can ensure that these nutrients are available when the body needs them most, maximizing their effectiveness.
Macronutrients and Anti-Aging
Macronutrients, such as protein, carbohydrates, and fats, all play critical roles in supporting cellular health and function. Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, including muscle tissue, which naturally declines with age. Consuming adequate protein throughout the day, especially around workouts, can help maintain muscle mass and strength.
Carbohydrates provide energy for bodily functions, including cellular repair processes. Choosing complex carbohydrates over simple sugars is important for sustained energy levels and overall health. Fats, essential for hormone production and cell membrane structure, also contribute to cellular health and function.
Micronutrients and Cellular Function
Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are essential cofactors in numerous biochemical reactions within the body. Adequate intake of vitamins and minerals, particularly antioxidants, is vital for combating oxidative stress, a major contributor to aging.
Antioxidants neutralize harmful free radicals, protecting cells from damage. Vitamin C, for example, is a powerful antioxidant that supports collagen production, vital for healthy skin and connective tissues. Consuming a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables is a great way to ensure a diverse intake of these vital micronutrients.
Exercise and Nutrient Timing
Exercise is a key component of any anti-aging strategy, and nutrient timing plays a crucial role in maximizing its benefits. Pre-workout nutrition can provide the energy needed for optimal performance and recovery. Post-workout nutrition is equally important for muscle repair and growth.
Timing nutrient intake around exercise can enhance muscle protein synthesis, leading to faster recovery and improved strength gains. Furthermore, strategic nutrient intake after exercise can help to replenish glycogen stores and reduce muscle soreness. This synergy between exercise and nutrient timing is a powerful tool in the fight against aging.
Sleep and Nutrient Utilization
Adequate sleep is critical for cellular repair and regeneration. During sleep, the body prioritizes restorative processes, including tissue repair and hormone regulation. Nutrient timing in relation to sleep can optimize the body's ability to absorb and utilize nutrients during this crucial phase.
Consuming nutrient-rich foods before bed can support these processes. Choosing foods that promote relaxation and digestion can contribute to a more restful sleep, which, in turn, enhances nutrient utilization and cellular repair.
Individualized Approaches to Nutrient Timing
While general guidelines exist for nutrient timing, individualized approaches are key to optimizing results. Factors such as age, activity level, and specific health conditions should be considered when creating a personalized nutrient timing plan. Consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional can help tailor a strategy that meets individual needs and goals.
Genetic predispositions and metabolic differences may impact how the body processes and utilizes nutrients, further highlighting the need for personalized strategies. This approach ensures that nutrient timing aligns with individual bio-individuality for maximum effectiveness and safety.
Micronutrients and Cellular Health

Essential Micronutrients for Cellular Function
Micronutrients, though present in smaller quantities compared to macronutrients, play crucial roles in maintaining cellular health and overall well-being. These essential vitamins and minerals are vital components of countless biochemical processes within the body. They act as catalysts, cofactors, and structural components, enabling cells to function optimally. Without adequate micronutrient intake, cellular processes can be compromised, leading to a range of health issues.
A balanced diet rich in micronutrients is essential for supporting various cellular functions, from energy production to DNA repair. The body cannot produce these vital nutrients on its own, so obtaining them through a diverse and nutritious diet is paramount.
Impact of Micronutrients on Cellular Metabolism
Micronutrients are directly involved in cellular metabolism, the process by which cells convert nutrients into energy. Specific vitamins and minerals act as cofactors for enzymes that facilitate metabolic reactions. For example, vitamin B12 is critical for the synthesis of DNA and RNA, essential components of cellular function. This influence on metabolic processes significantly impacts energy production and cellular growth.
Micronutrients and Cellular Communication
Cellular communication is essential for coordinating bodily functions. Micronutrients are involved in signaling pathways that regulate cellular responses to various stimuli. Certain minerals, like zinc, are critical for the proper functioning of receptors and transporters involved in cell-to-cell communication. This intricate network of communication is vital for maintaining homeostasis and responding to internal and external changes.
These processes ensure that cells can effectively respond to their environment and maintain the body’s overall health.
Micronutrient Deficiency and Cellular Damage
Inadequate intake of micronutrients can lead to a variety of cellular dysfunctions. Deficiencies can disrupt cellular processes, potentially leading to oxidative stress, inflammation, and DNA damage. This can ultimately compromise cellular structure and function, increasing the risk of various health problems, from weakened immune responses to impaired cognitive function. Addressing potential deficiencies is vital for maintaining cellular integrity and overall health.
A balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, is typically sufficient to meet the body's micronutrient needs.
Micronutrients and Cellular Repair Mechanisms
Micronutrients are also essential for supporting cellular repair mechanisms. Certain vitamins and minerals are crucial for the synthesis of collagen, a vital component of connective tissues. This is essential for wound healing and maintaining the structural integrity of various tissues throughout the body. Adequate intake of these nutrients is particularly important during times of stress or injury to support the body's natural repair processes.
Antioxidants, like vitamin C and E, play a crucial role in neutralizing harmful free radicals that can damage cells, thus promoting cellular repair and preventing premature aging.
Lifestyle Integration and Sustainability

Embracing Sustainable Practices
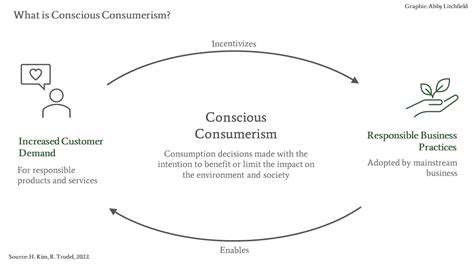
Integrating sustainable practices into your daily life is more than just a trend; it's a crucial step towards a healthier planet. Making conscious choices about your consumption patterns, from the food you eat to the products you buy, can significantly reduce your environmental footprint. This involves considering the entire lifecycle of a product, from its production to its disposal, and making informed decisions that prioritize environmental responsibility. Minimizing waste, opting for reusable items, and supporting businesses with ethical and sustainable practices are all important components of this lifestyle shift.
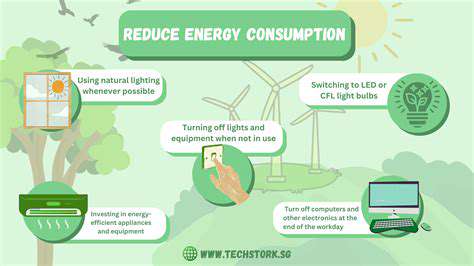
Sustainable living encompasses a wide range of actions. From reducing water and energy consumption at home to choosing eco-friendly transportation options, every small step contributes to a larger positive impact. By understanding the interconnectedness of our actions and their effects on the environment, we can cultivate a deeper sense of responsibility and make a difference. This mindful approach extends beyond individual choices and encourages collective action to create a more sustainable future for everyone.
Prioritizing Well-being and Environmental Harmony
A key aspect of lifestyle integration is prioritizing well-being and recognizing the direct link between environmental health and personal health. Choosing organic foods, minimizing exposure to harmful chemicals, and supporting local farmers contribute not only to a healthier environment but also to a healthier you. Sustainable practices often align with prioritizing natural and wholesome ingredients, leading to improved physical and mental well-being.
Furthermore, prioritizing well-being extends to our connection with nature. Spending time outdoors, engaging in activities like gardening, or simply appreciating the beauty of the natural world can foster a deeper appreciation for the environment and motivate us to protect it. This connection with nature can also offer significant mental and emotional benefits, reducing stress and promoting overall well-being. Finding balance between our personal needs and the health of the planet is crucial for long-term well-being.
Building a Sustainable Community
Integrating sustainable practices is not a solitary endeavor; it's about building a sustainable community. Supporting local businesses that prioritize ethical and sustainable practices is a powerful way to foster change. These businesses often employ environmentally conscious methods, use recycled materials, and prioritize fair labor practices. By choosing to support them, we're directly impacting the positive change they're already making.
Encouraging others to adopt sustainable practices through education and awareness is another crucial element of building a sustainable community. Sharing information and resources, hosting workshops, and participating in local initiatives can inspire others to join the movement. This collaborative approach amplifies the impact of individual choices and creates a ripple effect of positive change across the community. Ultimately, a sustainable community is built on shared responsibility and mutual support for a healthier future.